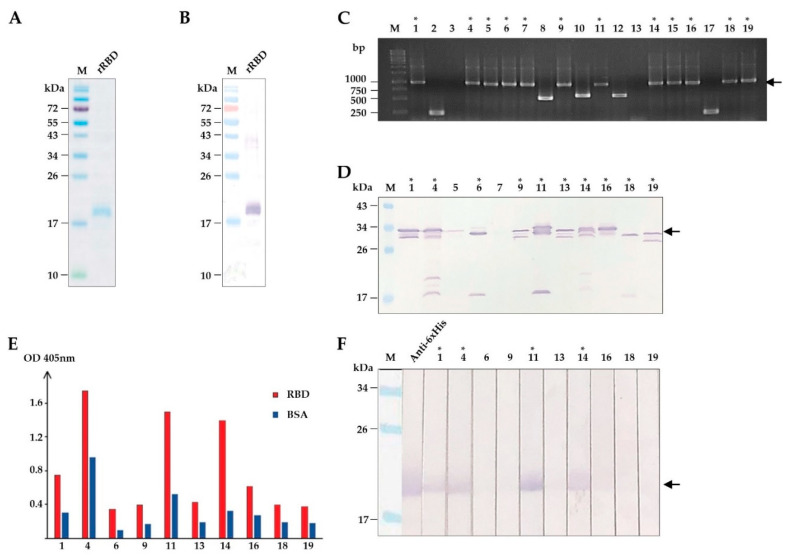
Figure 1.
Production of recombinant (r) RBD and selection of HuscFvs that bind to rRBD. (A) SDS-PAGE-separated and CBB stained purified rRBD. (B) Western blot pattern of rRBD that corresponds to lane rRBD in (A) detected by anti-6X His antibody. (C) Screening of phage-infected E. coli clones that contained rRBD-bound phage clones for huscfvs by PCR. Arrowhead indicates the expected amplicon of intact huscfvs about 1000 base pairs (bp). (D) Screening of soluble HuscFvs contained in the lysates of E. coli carrying huscfv-phagemids by Western blotting. Asterisks indicate the clones that produced HuscFvs. Arrowhead indicates the expected molecular mass of HuscFvs about 30–35 kDa. (E) Binding assay of soluble HuscFvs in E. coli lysates to rRBD by indirect ELISA, using BSA as the control antigen. (F) Binding assay of soluble HuscFvs in E. coli lysates to rRBD blotted onto nitrocellulose strips. Asterisks indicate the clones that their HuscFvs bound to rRBD. Arrowhead indicates the rRBD-HuscFv reactive bands. Lane Anti-6× His was rRBD probed with anti-6X His antibody that served as a positive control for rRBD binding. The number on each lane in (C,D,F) indicates the number of the phage-transformed E. coli clone. The asterisks in (C,D,F) indicate HuscFv-displayed phage-infected E. coli clones that carried intact huscfvs, expressed soluble HuscFvs, and produced rRBD-bound HuscFvs, respectively. Lanes M and numbers on the left of (A,B,D,F) are protein molecular mass marker and protein molecular weights in kDa, respectively. Lane M and numbers on the left of (C) are DNA ladder and DNA sizes in bp, respectively.