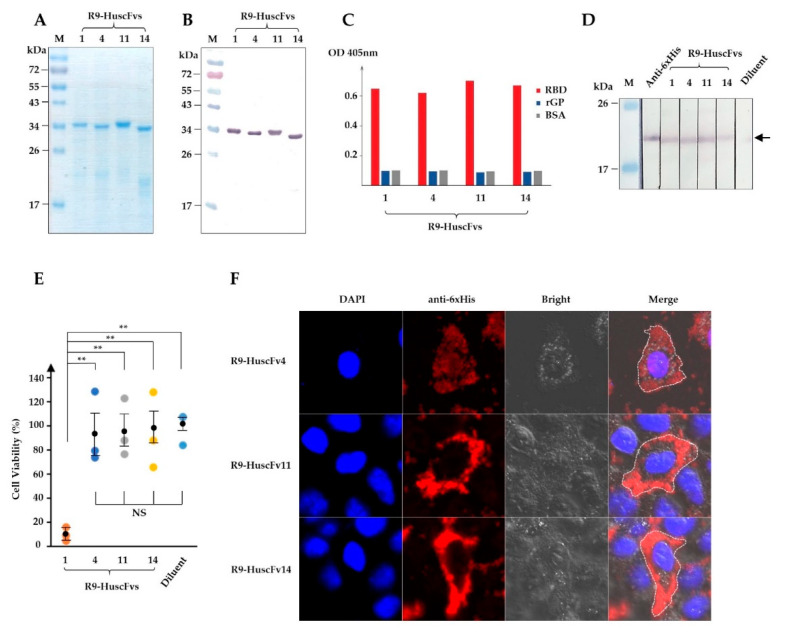
Figure 2.
Production of R9-HuscFvs and their rRBD binding activity, biocompatibility to human cells, and cell-penetrating ability. (A) R9-HuscFvs were produced, purified, and verified by SDS-PAGE and CBB staining. (B) Western blotting of R9-HuscFvs that corresponds to (A), detected by anti-6× His antibody. (C) Binding of R9-HuscFvs to rRBD and recombinant full-length GP (rGP) by indirect ELISA. (D) R9-HuscFvs binding activity to rRBD blotted onto nitrocellulose strips. Arrowhead indicates the rRBD-R9-HuscFvs reactive bands. (E) Analysis of R9-HuscFv-mediated cellular cytotoxicity to HEK293T cells incubated overnight with 30 μg/mL of R9-HuscFvs or equivalent volume of antibody diluent. Results are shown as mean ± standard error of percent cell viability of three independent experiments in duplicates. **, p < 0.01; NS, not significantly different. (F) Cell-penetrating ability (intracellular localization) of R9-HuscFvs in HEK293T cells incubated with 30 µg/mL of R9-HuscFvs for 24 h, as observed by confocal microscopy. Each image shown is a representative of a 1-µm section from a series of z-stack analysis. Lanes M and numbers on the left of (A,B,D) are the protein molecular weight marker and protein molecular masses in kDa, respectively.