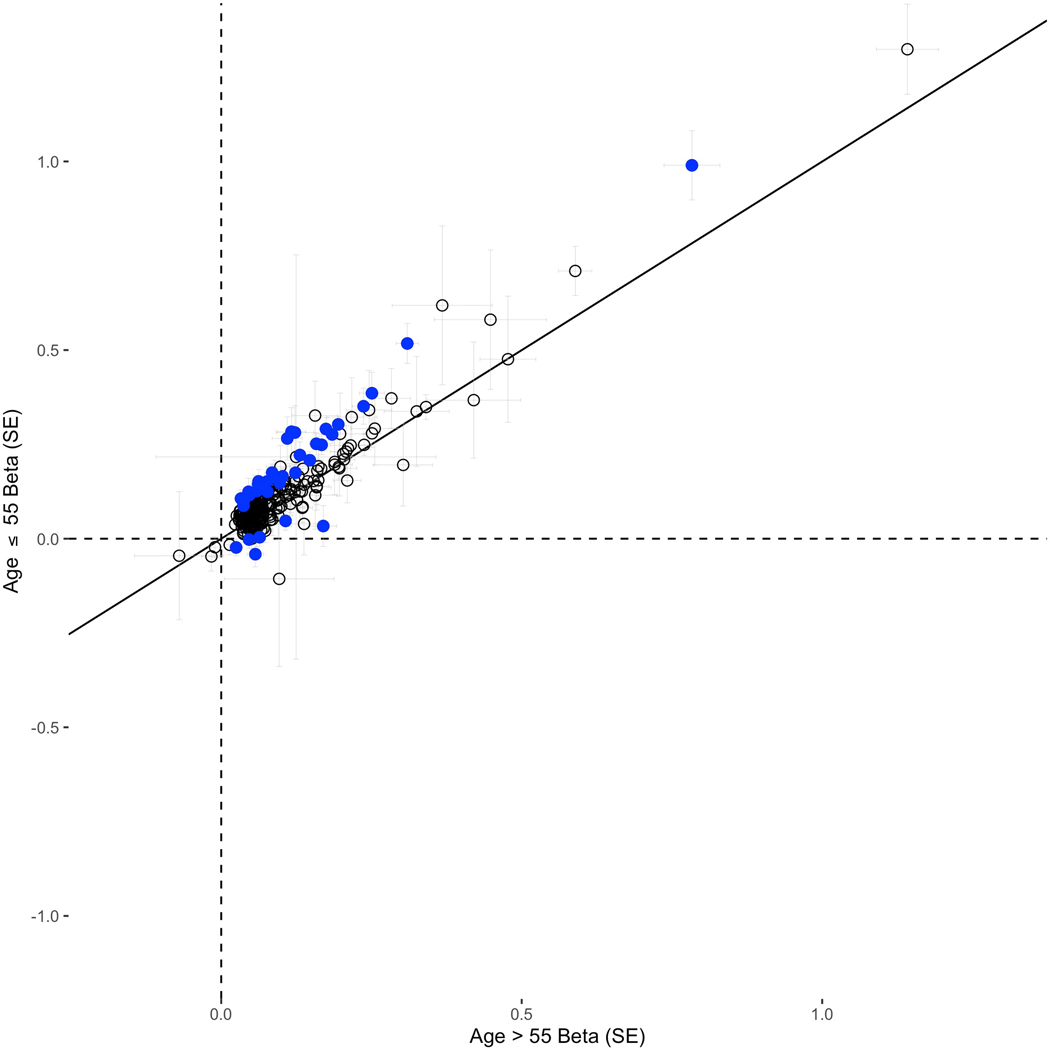
Extended Data Fig. 1. Effect comparisons of the 269 prostate cancer risk variants between younger (age≤55) and older (age>55) men of European and African ancestry.
Variants above the identity line have larger effects in younger men, and variants below the identity line have larger effects in older men. Blue dots indicate effect differences with an unadjusted P-value < 0.05. 188/269 (69.9%) of tested variants have larger effects in younger vs. older men and 31/269 (11.5%) of tested variants have larger effects in younger vs. older men at a P-value < 0.05 threshold. All statistical tests were two-sided. Results presented figure are also provided in Supplementary Table 8. SE: standard error.