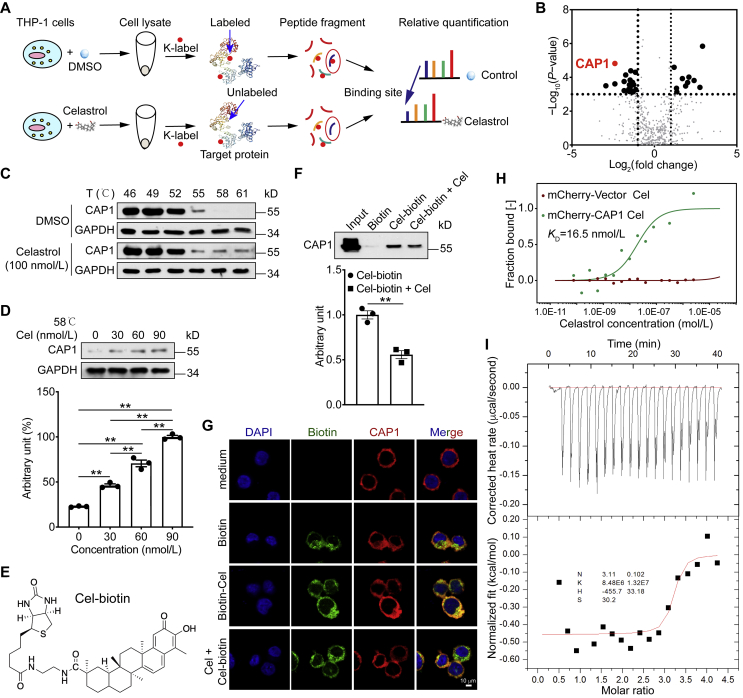
Figure 5.
Celastrol binds adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 (CAP1) protein. (A) Schematic representation of the TRAP experiment. (B) Celastrol binding proteins using target-responsive accessibility profiling (TRAP) experiment. (C) and (D) Cells were incubated with celastrol or DMSO for 2 h, and cellular thermal shift assays (CETSA) analyzed the thermal stabilization of CAP1 protein at different temperatures and concentrations. (E) Chemical structure of the biotin labeled celastrol (Cel-biotin). (F) Cel-biotin was added to streptavidin-agarose beads and incubated. Biotin alone was used as a control. Lysates prepared from THP-1 cells were added to the streptavidin-agarose beads with Cel-biotin. Eluent was then loaded on a polyacrylamide gel for Western blot analysis. Total lysates were used as an input control. (G) Immunofluorescence staining of phorbol ester (PMA)-differentiated THP-1 cells were treated with celastrol for 2 h, and then stimulated with biotin or Cel-biotin for 4 h. (H) The interaction of celastrol with CAP1 or vector was measured by microscale thermophoresis (MST). The KD value of celastrol and CAP1 interaction was determined with MO.Affinity Analysis Software. (I) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) enthalpogram of the interaction between celastrol and CAP1 at 25 °C. The titration curve is depicted as a function of the molar ratio between CAP1 and the calculated concentration of celastrol in the assay. Data represent as mean ± SEM. P values are determined by two-tailed Student's t test (n = 3). ∗∗P < 0.01.