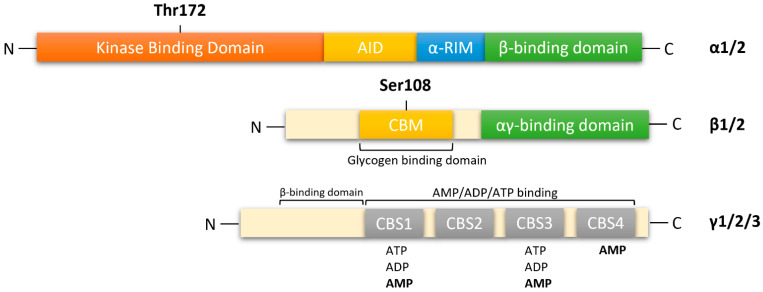
Figure 1.
Functional domain of AMPK subunits. AMPK is a heterotrimeric complex composed of a catalytic α subunit(α1/2), regulatory β subunit (β1/2), and γ (γ1/2/3) subunit. AMPKα: kinase domain (KD) at the N-terminal contains Thr172, which is phosphorylated by upstream kinases; AID, auto-inhibitory domain; α-RIM: regulatory subunit interacting motif triggering conformational changes; β-subunit binding domain at the C-terminal. AMPKβ subunit: carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) near the N-terminal contains Ser108, which is important for the mechanism of action of some direct activators of AMPK; C-terminal domain containing the α-subunit-binding site and immediately followed by the domain for the γ-subunit interaction. αγ-binding domain: α-subunit-binding and γ-subunit interaction site at the C-terminal. AMPKγ subunit: cystathione-β-synthases (CBS) domain, which forms two Bateman domains containing four ATP/ADP/AMP-binding sites (CBS1–4).