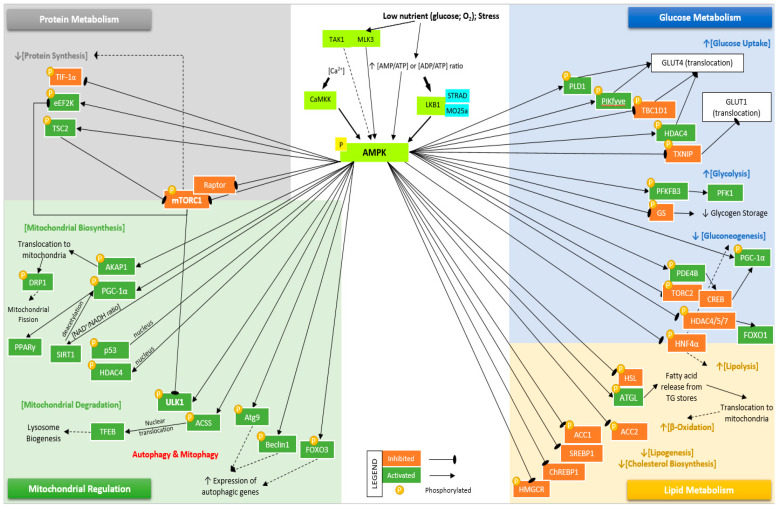
Figure 3.
Summary of differentially expressed genes involved in the AMPK signaling pathway. Activation of AMPK occurs following phosphorylation of Thr172 (not shown) by LKB1, CaMKK, TAK1, and MLK3. Activated AMPK regulates glucose metabolism by increasing glucose uptake via translocation of GLUT4 by phosphorylating/inhibiting TBC1D1 and phosphorylating/activating PIKfyve, HDAC4, and PLD1. AMPK-mediated translocation of GLUT1 occurs following phosphorylation/inhibition of TXNIP. Glycolysis is stimulated via activation of PFKFB3, and glycogen storage is reduced by inhibition of GS. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis occurs following phosphorylation/inhibition of PDE4B, TORC2, HDAC4/5/6, and HNF4α. AMPK regulates lipid metabolism by phosphorylating/inhibiting HSL, HNF4α, and activating ATGL to increase lipolysis. An increase in β-oxidation occurs by phosphorylation of ACC2 and reducing fatty acid synthesis by phosphorylation of ACC1. AMPK decreases lipid and sterol synthesis by phosphorylating/inhibiting SREBP1, ChREBP, and HMGCR. AMPK inhibits protein synthesis by phosphorylating/inhibiting TIF-1α, mTORC1, and RAPTOR, and phosphorylating/activating eEF2K and TSC2, which inhibit mTORC1. Lastly, mitochondrial functions are regulated by activated AMPK by activating mitochondrial biosynthesis. AMPK phosphorylates/activates AKAP1, DRP1, PGC-1α, SIRT1, p53, and HDAC4. AMPK activates mitophagy and autophagy pathways by phosphorylating/activating ULK1, ACSS, Atg9, Beclin1, and FOXO3.