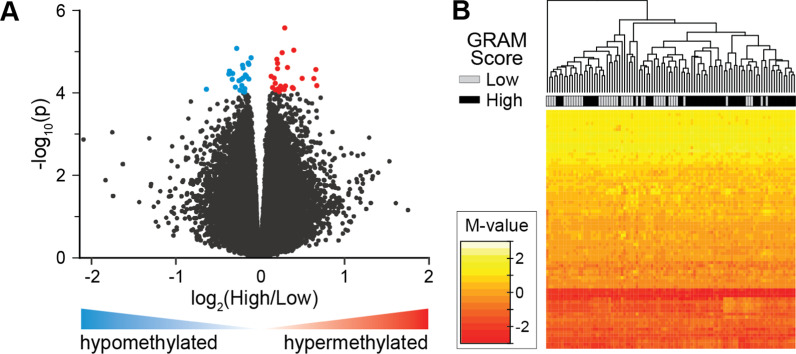
Fig. 6.
DNA methylation is associated with COVID-19 outcomes. A Volcano plot shows genes associated with dichotomized GRAM-risk scores, either hyper-methylated (red) or hypo-methylated (blue). B DNA methylation levels at 77 differentially methylated positions (DMPs) correlate with disease severity in COVID-19 patients. DMRs (N = 19) associated with the GRAM-score were identified in COVID-19 patients (N = 100). DMRs were ascertained as regions with at least 3 consecutive CpGs where > 75% of the CpGs in the region had a FDR p value < 0.05 and all were either hyper-methylated or hypo-methylated. DNA methylation levels of the DMPs (N = 145) residing in the DMRs were subjected to recursive feature elimination to identify CpGs that best distinguish GRAM-score risk. Shown is a hierarchical cluster using the DNA methylation data from the 77 DMPS (see Additional file 1: Table S8), that are shown as a heatmap of the M-values. Low GRAM-score risk (gray) and high GRAM-score risk (black) are indicated. These results indicate that DNA methylation levels at these 77 DMPs may be useful as biomarkers of the severity of COVID-19 patients. (see Additional file 1: Table S6-1 and S6-2)