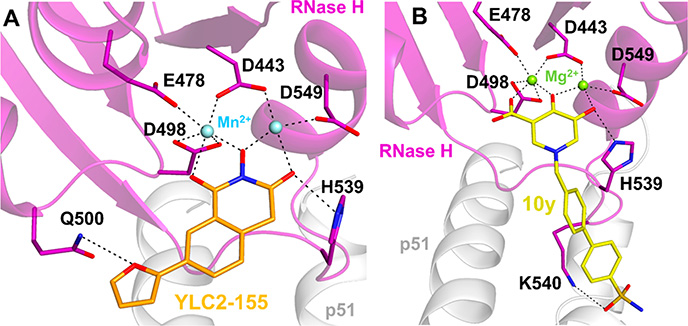
Figure 14.
Interactions of RNase H inhibitors (RNHIs) at the RNase H active site of HIV-1 RT. (A) A 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3-dione RNHI, YLC2–155 (orange sticks), chelates two Mn2+ ions (light-blue spheres) that are bound by conserved RNase H active site residues D443, E478, E498, and D549. YLC2–155 also forms hydrogen bond interactions with Q500 and H539 (PDB 5UV5). YLC2–155 can also bind to the RNase H active site in a different conformation, with the furan ring pointing toward H539 (not shown). Based on ref 252. (B) A hydroxypyridonecarboxylic acid RNHI, 10y (yellow sticks), chelates two Mg2+ ions (light-green spheres) that are bound by the conserved RNase H active site residues. 10y also forms hydrogen bond interactions with H539 and K540 (PDB 5J1E). Based on ref 256.