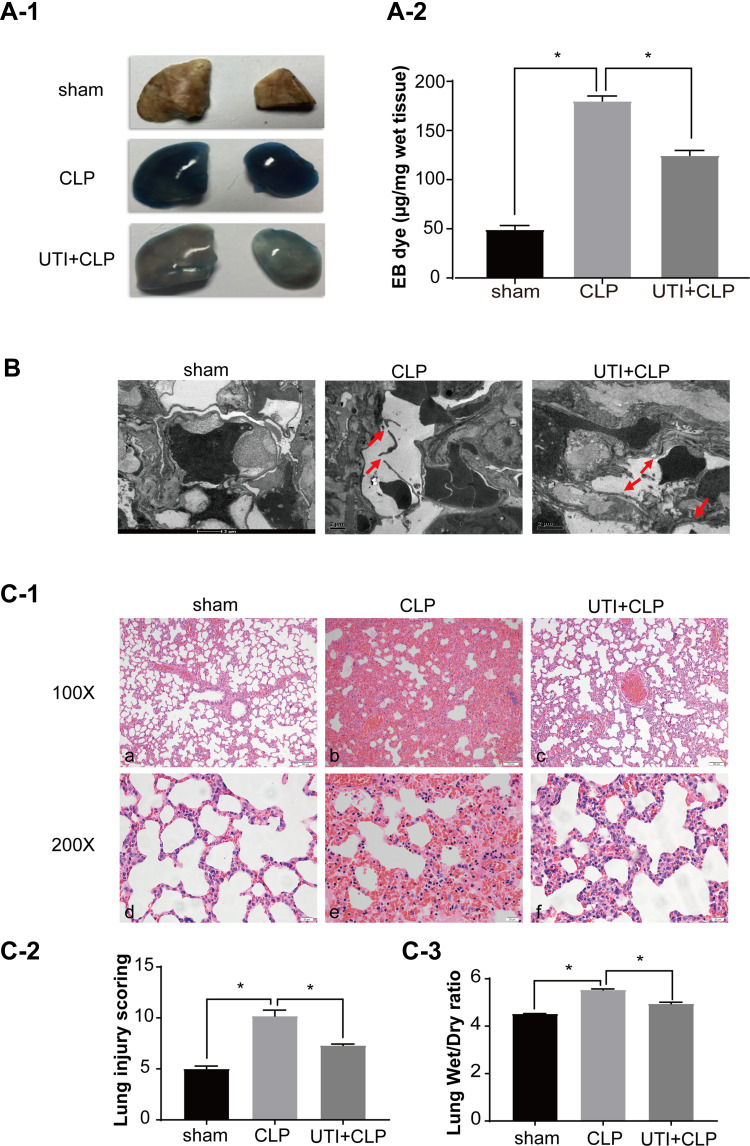
Figure 7.
UTI repaired the barrier structure and relieved pulmonary capillary endothelial leakage in CLP-induced rat lungs. In the CLP group, EB inundated the lung tissue, while it was noticeably reduced in theUTI+CLP group (A). Electron microscope (B) showed that the barrier structure of CLP-induced rats was severely damaged (red arrow) when compared with the sham group; the gaps between endothelial cells were evidently narrowed and the barrier structure was reversed in the UTI+CLP group. Histopathological morphology was assessed by performing hematoxylin and eosin staining (C-1). The lung W/D ratio varied in different groups of rats (C-3). In the CLP group, severe pulmonary edema, interstitial hemorrhage, alveolar collapse, a large number of inflammatory cell infiltration (C-1b,e), higher lung injury score (C-2) and W/D ratio (C-3) occurred. Compared with the CLP group, the UTI+CLP group showed less destruction of lung structure (C-1c,f), lower lung injury score (C-2) and lower W/D ratio (C-3). *p<0.05.
Abbreviation: W/D, wet to dry.