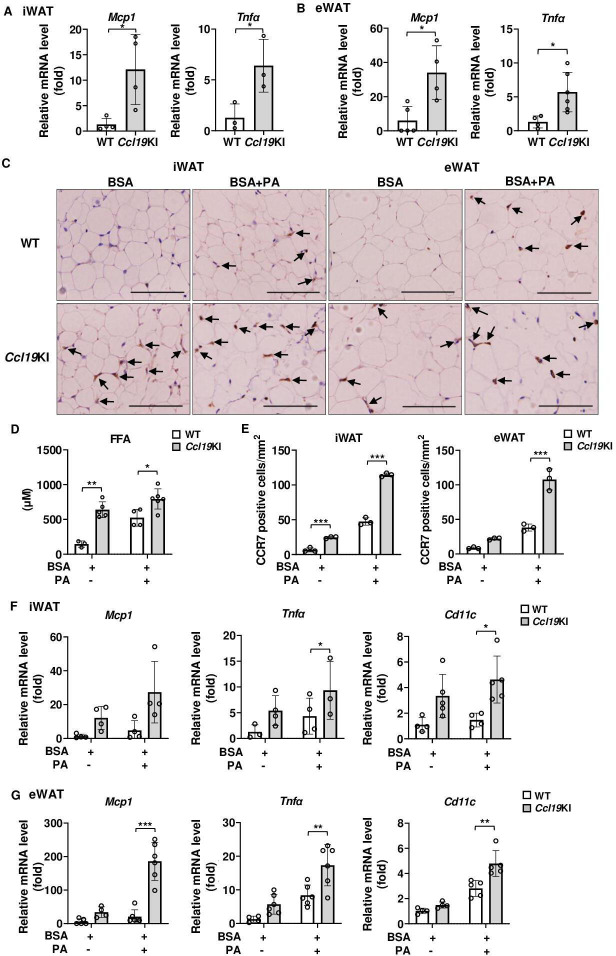
Figure 6.
Expression of proinflammatory-related gene in iWAT and eWAT of Ccl19KI mice, and the effects of PA injection on these gene expression. All mice were fed with a normal diet (ND) after weaning. (A, B) Relative mRNA expression level of Mcp1 and Tnfα in iWAT (A) and eWAT (B) of WT and Ccl19KI mice was measured by RT-PCR. Data are expressed as fold changes in the expressions of each gene relative to Gapdh (n=3–5). (C–G) Tissue and blood samples of WT and Ccl19KI mice were collected 12 hours after a single intraperitoneal injection of palmitic acid (PA). (C) Serum FFA concentration was measured by the method as described. (D) Images of immunohistochemical staining for CCR7 of adipose tissue. Positive area appears brown color. Images were representative from three samples of each group. Scale bar, 100 µm for 40× magnification. (E) Quantification of CCR7-positive cells of immunohistochemical staining (n=3 per group, with three random fields per animal). (F, G) Relative expression level of proinflammatory-related genes in iWAT (F) and eWAT (G) was determined by RT-PCR. Data are expressed as fold changes in the expressions of each gene relative to Gapdh (n=3–5). Note PA injection further enhanced the effects of CCL19. n=3 to 5 per group. Data are expressed as mean (SD). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. BSA, bovine serum albumin; CCL19, C-C motif ligand 19; CCR7, CC-chemokine receptor 7; eWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; FFA, free fatty acid; iWAT, inguinal white adipose tissue; KI, knock-in; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; WT, wild type.