FIGURE 1.
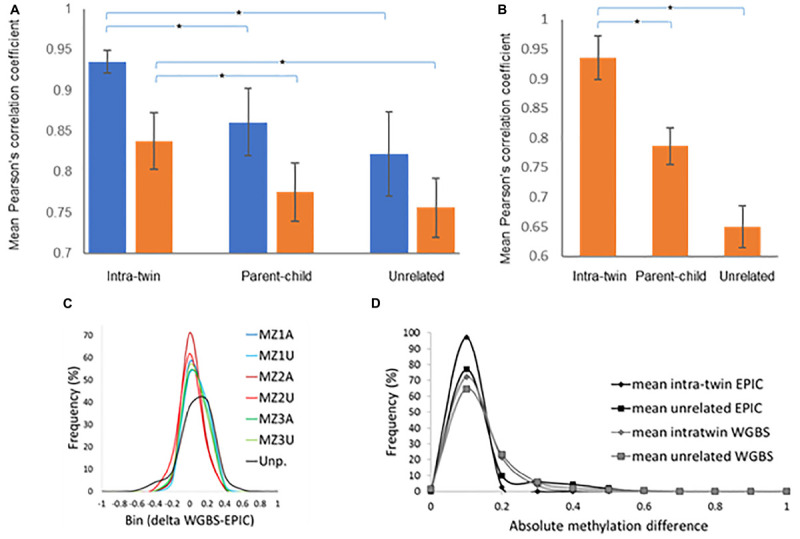
MZ co-twins are highly correlated for DNA methylation but have site-specific differences. (A) Pearson’s correlation coefficients derived from comparing intra-twin, parent-child and parent to parent (unrelated) methylation levels at 100X (blue) or 30X (brown) genome coverage. (B) Correlation coefficients using only variable CpGs as identified by Feinberg et al. (2010) at 30X genome coverage. (C) Comparison between DNA methylation values for 16,920 individual CpG loci generated by MethylationEPIC microarray and whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. Methylation values generated by Rnbeads for the MethylationEPIC microarray were subtracted from methylation levels calculated from the sequencing data for the same sample (MZ1A to MZ3U). Averaged comparisons contrasting EPIC and WGBS data from unpaired (Unp.) samples is also included (black line). (D) Distribution of average absolute differences in DNA methylation within the MZ twins as well as comparisons of unrelated individuals. A significantly (P<1.2e-10 for WGBS and P<1.9E-12 for EPIC, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test) smaller number of CpG sites with a large average within-twin differences in methylation level was observed in within twin comparisons as contrasted with comparisons of unrelated individuals (unaffected-unaffected, NSCLP-unaffected (inter-twins) or NSCLP-NSCLP).
