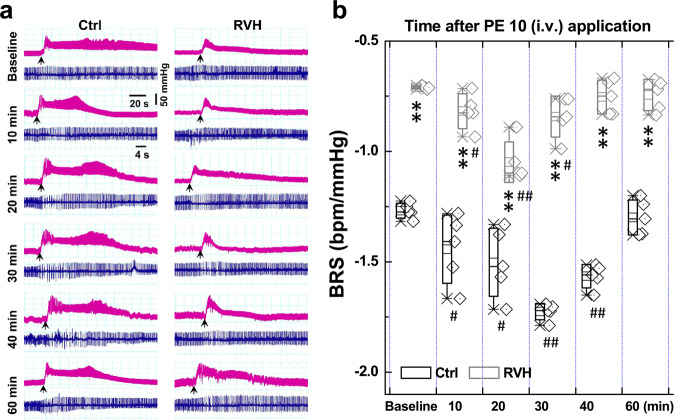
Fig. 1. Acute effect of NaHS on baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) under control and hypertensive conditions (renovascular hypertension, RVH).
A femoral artery catheter was connected to a transducer to measure the change in MAP, and a venous cannula was used to administer NaHS and PE. a Representative recordings of MAP collected from control (Ctrl, n = 5) and RVH (n = 5) rats in the presence of 10 μg· kg−1 PE before (baseline) and after (10–60 min) the intravenous injection of 0.67 mg ·kg−1 NaHS. Representative recordings of heart rate (HR) along with changes in blood pressure (BP). b The summarized changes in BRS (ΔHR/ΔMAP, bpm/mmHg) upon treatment with PE (10 μg ·kg−1) before (baseline) and after (10–40 min) NaHS injection. The averaged data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. baseline of the Ctrl or model group; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. the Ctrl group.