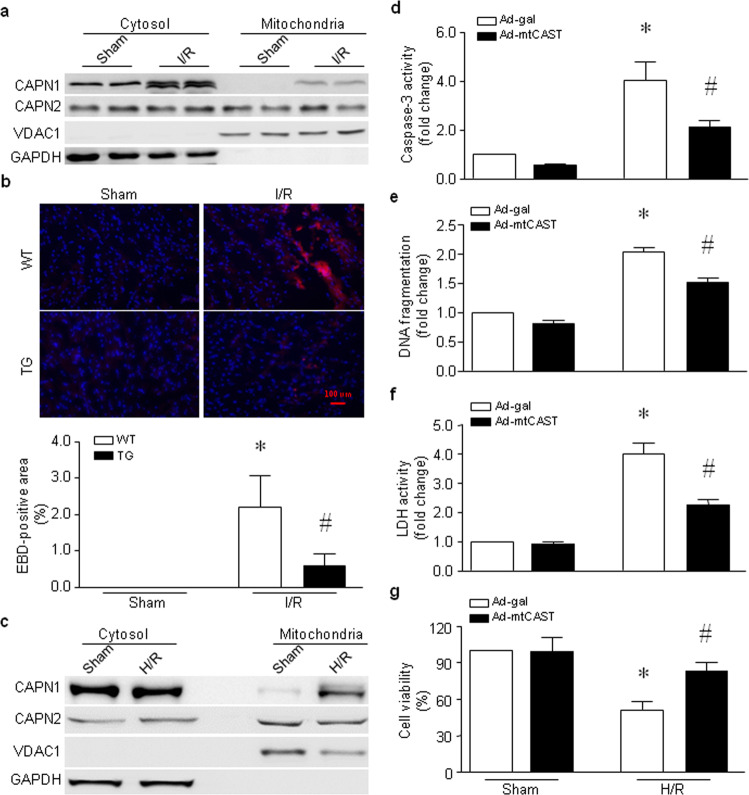
Fig. 3. Roles of mitochondrial calpain in mouse hearts subjected to global I/R and H9c2 cells following H/R.
a, b Hearts isolated from adult Tg-mtCAST/tTA (TG) mice and their wild-type (WT) littermates were subjected to 45 min of global ischemia and 30 min of reperfusion. a Heart tissues were collected, and mitochondria were isolated. Representative Western blots for CAPN1, CAPN2, VDAC1, and GAPDH from two out of the five hearts are shown. b Necrotic cell death was determined by Evans blue dye staining. The upper panel is a representative microphotograph of Evans blue staining (red) and nuclear staining (blue), and the bottom panel is the quantitation of the percentage of the Evans blue-positive area relative to the total area (%). The data are presented as the mean ± SD of five different hearts from each group. *P < 0.05 vs WT+sham and #P < 0.05 vs WT+I/R. c–g H9c2 cells were infected with Ad-mtCAST or Ad-gal for 24 h and then subjected to 24 h of hypoxia followed by 24 h of reoxygenation (H/R). H9c2 cells were collected, and mitochondria were isolated. c A representative Western blot for CAPN1, CAPN2, VDAC1, and GAPDH from the three experiments. Apoptosis was determined based on caspase-3 activity (d) and DNA fragmentation (e). f The LDH level in the culture medium was measured. g Cell viability was determined. The data are the mean ± SD from three different experiments. *P < 0.05 vs Ad-gal + sham and #P < 0.05 vs Ad-gal + H/R.