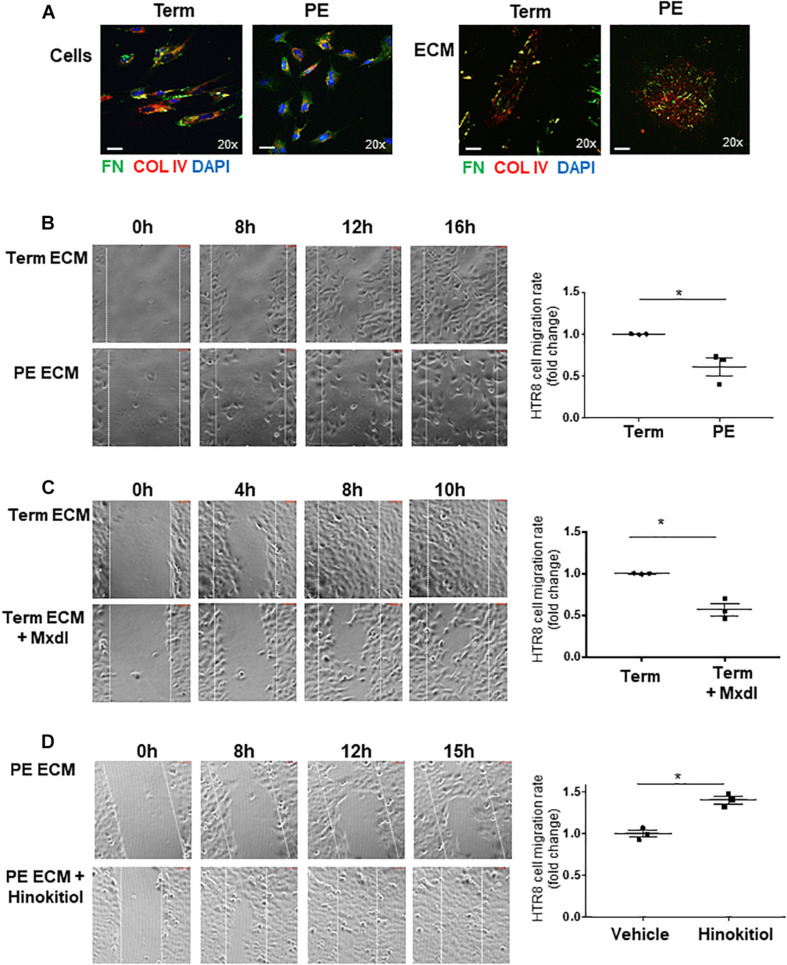
FIGURE 7.
Defects in ECM deposited by PE pMSCs impedes extravillous trophoblast cell migration in vitro. (A) IF analysis of FN (green) and COL IV (red) in TC and PE pMSCs prior to (top panel) and following ECM extraction (bottom panels). Scale bars at 20× magnification represent 2.2 μM. Representative of three separate pMSC isolations. (B) Images and associated quantification (expressed as a migration index fold changes relative to control) of HTR-8/SVneo cell migration over time on TC or PE pMSC-deposited ECM, captured by time-lapse microscopy; n = 3 separate pMSC isolations per group. (C) Snapshot images and quantification of HTR-8/SVneo cell migration over time on ECM deposited by TC pMSCs treated with vehicle control (95% EtOH) or minoxidil (Mxdl). n = 3 separate pMSC isolations. (D) Representative images and quantification of HTR-8/SVneo cell migration over time on ECM deposited by PE pMSCs treated with control vehicle (DMSO) or 1 μM Hinokitiol, captured by time-lapse microscopy; n = 3 separate pMSC isolations. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05 (unpaired Student’s t-test).