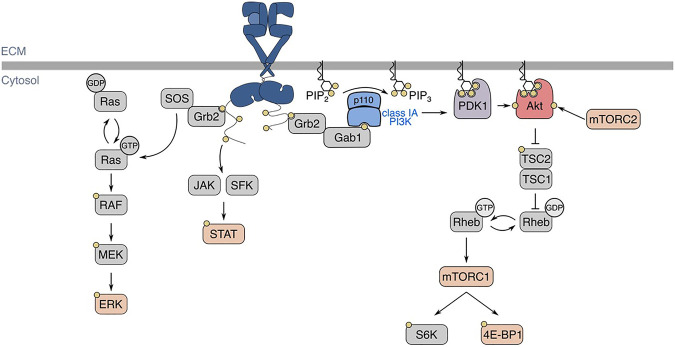
FIGURE 2.
EGFR structure, ligand-binding, and signaling pathways. In the basal state, EGFR exists in an autoinhibited conformation. Ligand-binding allows for the formation of homo- or heterodimers, which activates EGFR intrinsic tyrosine kinase domains and ensues signal transduction, shown here as an EGFR homodimer with one ligand bound. Various signalling pathways are initiated by the active EGFR, such as Ras-Erk, JAK/SFK-STAT, and PI3K-Akt. Regarding EGFR-PI3K-Akt signalling, EGFR autophosphorylation at Y1068 allows for the activation of class IA PI3K. The active PI3K subsequently phosphorylates PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2) into PI(3,4,5)P3, which recruits kinases PDK1 and Akt to the plasma membrane. There, Akt is phosphorylated by PDK1 and mTORC2 at T308 and S473, respectively. EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor, JAK: Janus kinase, SFK: Src-family kinase, STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription, PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase, PDK1: phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1, mTORC: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex, TSC: tuberous sclerosis complex, SOS: son of sevenless, Grb2: growth factor receptor-bound protein 2, Gab1: Grb2-associated binding protein 1.