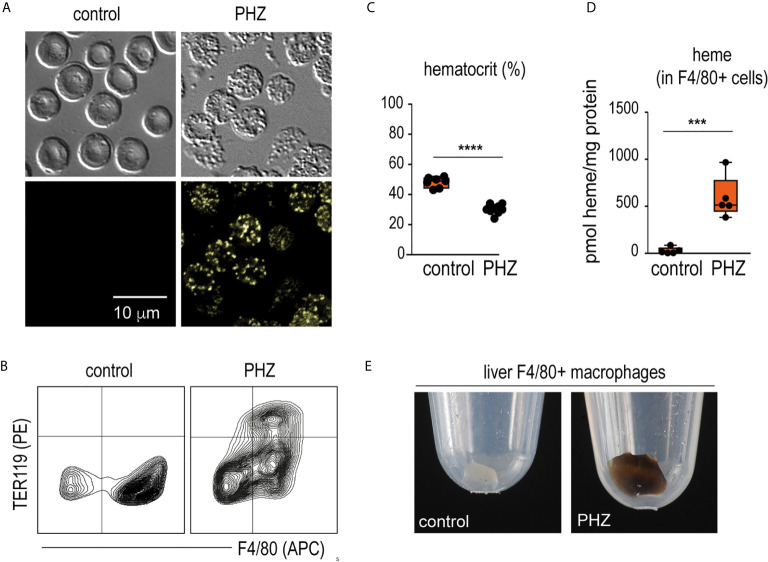
Figure 1.
PHZ administration induces acute erythrophagocytosis in F4/80+ liver macrophages C57Bl/6J mice were treated with saline (control) or phenylhydrazine (PHZ, 90 mg/kg) and sacrificed 24 or 48 h later for blood and organ collection. (A) RBCs of saline- and PHZ-treated C57Bl/6J mice. Upper panels: DIC brightfield image at 600x magnification, lower panels: autofluorescence of Heinz bodies in the green fluorescence channel. (B) Representative flow cytometry density plots of liver cells stained for F4/80 and intracellular TER-119 and gated from CD45+ liver cells. Data were obtained from a control mouse and a mouse after PHZ treatment. (C) Hematocrit of saline- and PHZ-treated mice at 48 h (n = 7–10). (D) Heme concentrations in purified F4/80+ liver macrophages isolated by positive selection using anti-F4/80 antibody coated magnetic beads, followed by magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) from control and PHZ-treated mice (n=5). Heme concentration was normalized to total protein levels in each group. No significant difference in total protein levels was observed between groups. (E) Representative photographs of cell pellets of purified F4/80+ liver macrophages from saline- and PHZ-treated mice. Individual symbols represent one mouse; ****p < 0.0001 and ***p < 0.001.