Figure 2. Myosin family members with roles in Filopodia, Microvilli and Stereocilia.
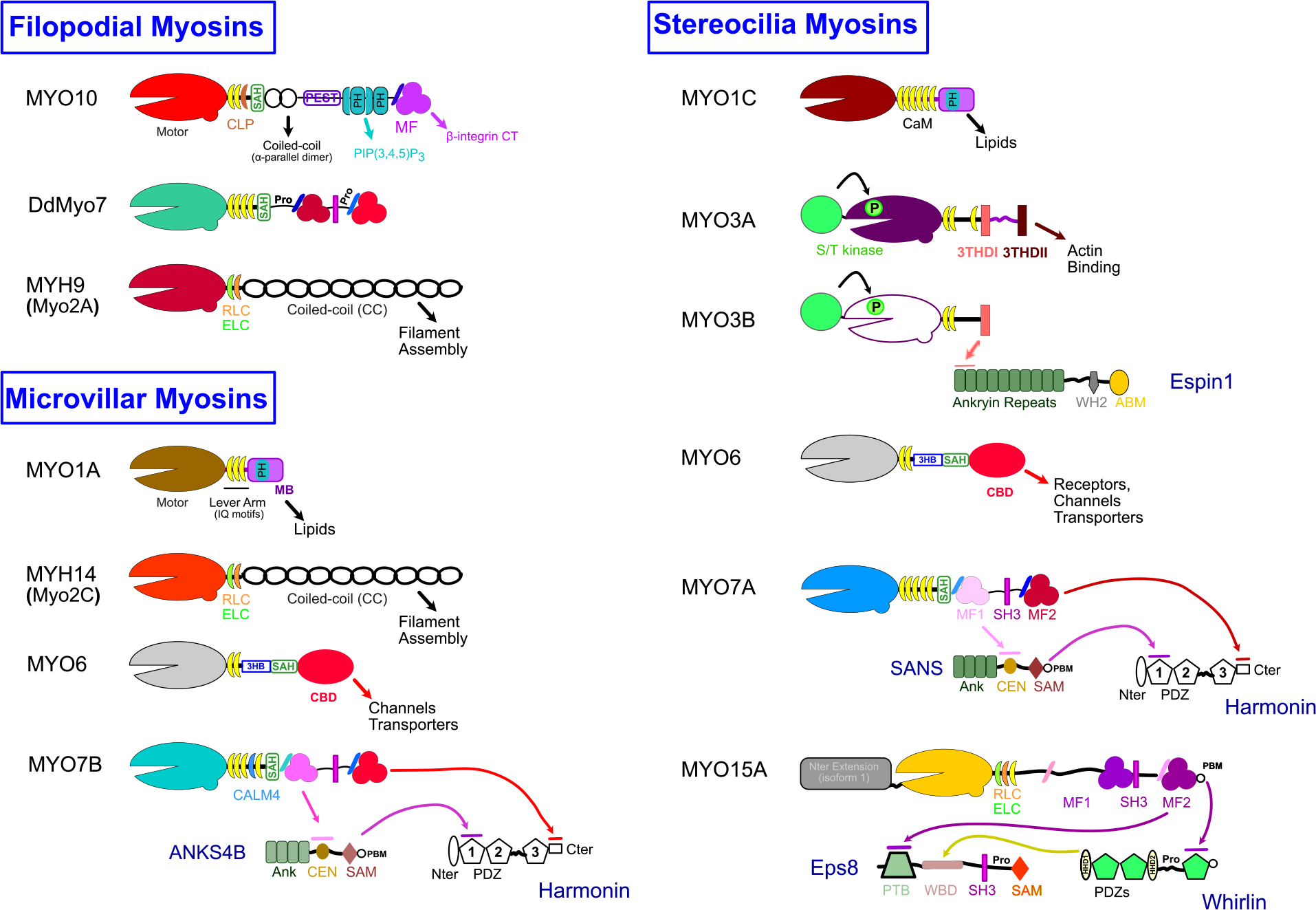
Cartoon schematics illustrating the key domains and features of diverse myosin motors. Key features are annotated and interactions between domains and partners or targets are indicated with arrows. Note that some myosins may use other light chains (LCs) in addition to calmodulin (CaM), including essential and regulatory LCs (ELC, RLC), calmodulin-related LC (CALM4, CLP). SAH, stable α-helix; PEST, proline (P), glutamic acid ( E), serine (S), and threonine (T) rich sequence; PH, plekstrin homology; MF, MyTH4-FERM; PIP(3,4,5)P3, Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; MB, membrane binding; 3HB, three-helix bundle; CBD, cargo binding domain; S/T kinase, serine/threonine kinase; 3THDI/II, tail homology domain I or II; SH3, src homology 3; CT, cytoplasmic tail; Ank, Ankryin repeat region; CEN, central domain; SAM, sterile alpha motif; PBM, PDZ binding motif; Nter/Cter, N-terminus and C-terminus; PDZ, post synaptic density protein (PSD95), Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor (Dlg1), and zonula occludens-1 protein (zo-1); WH2, Wasp homology 2; ABM, actin binding module; PTB, phosphotyrosine binding domain; WBD, whirlin binding domain; Pro, Proline-rich; HHD, harmonin homology domain.
