Figure 4. The Myosins of Microvilli.
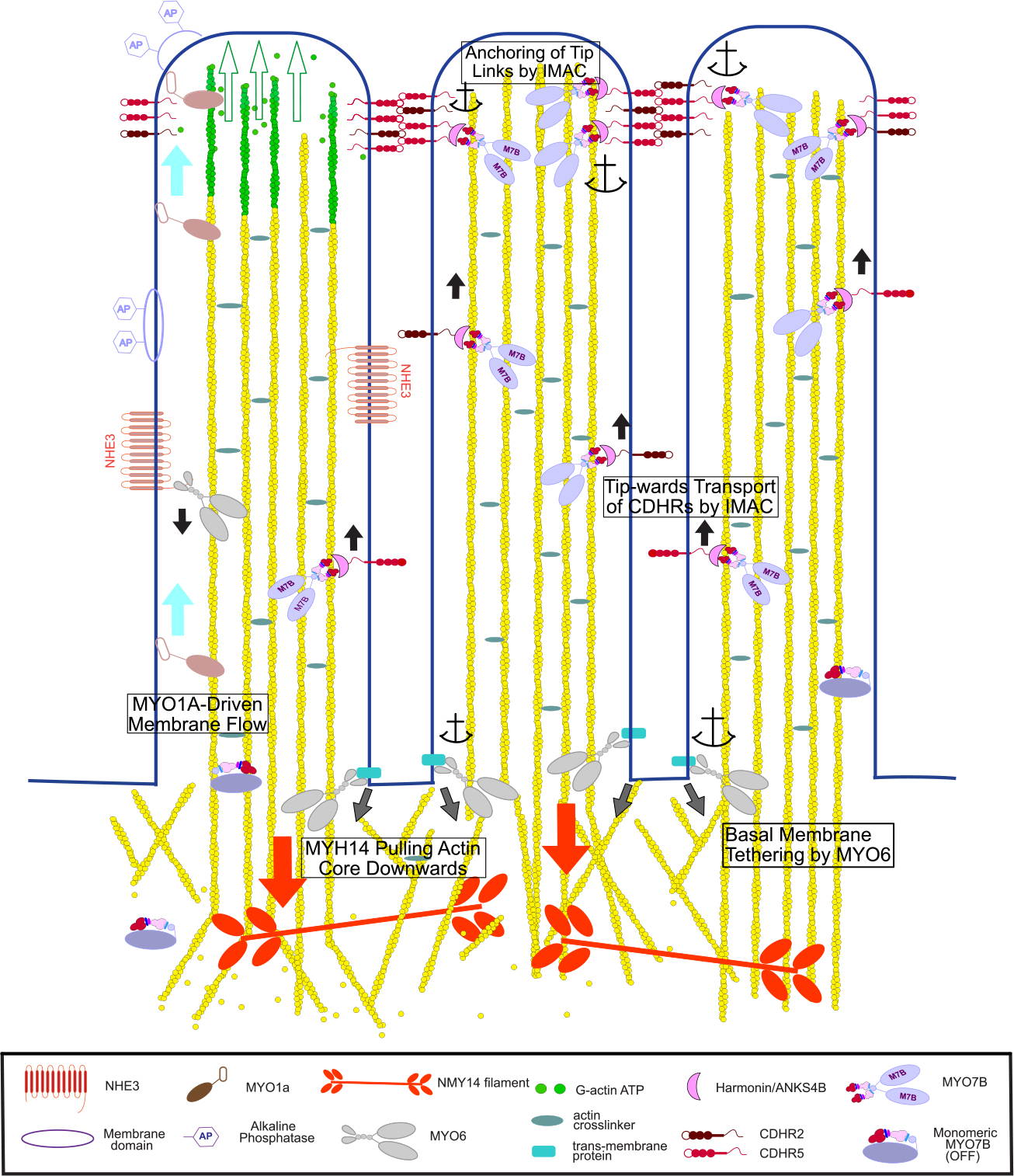
Conceptual model of the diverse functions carried out by the different microvillar myosins. These include generation of membrane flow by MYO1A (light blue arrows) that leads to shedding of membrane vesicles containing alkaline phosphatase (AP). Green arrows indicate extension of microvillus as monomers are added to the tip. MYO6 transports channels down to the base of the microvillus, such as NHE3 as shown here, and also keeps the basal plasma membrane between the microvilli tightly anchored to the actin cortex (grey arrows). MYO7B-Harmonin-ANKSB may move component of the IMAC complex including Harmonin, ANKS4B, CDHR2 and CDHR5 cadherin up toward the microvilli tip (black arrows). There, an IMAC condensate that includes MYO7B could anchor the cadherins in place thus stabilizing the inter-microvilli links. Non-muscle MYO2C links actin rootlets and provides a downward pulling force (red arrows) balanced by polymerization at the microvilli tip to maintain proper microvilli length.
