Figure 5. Functions of Stereocilia Myosins.
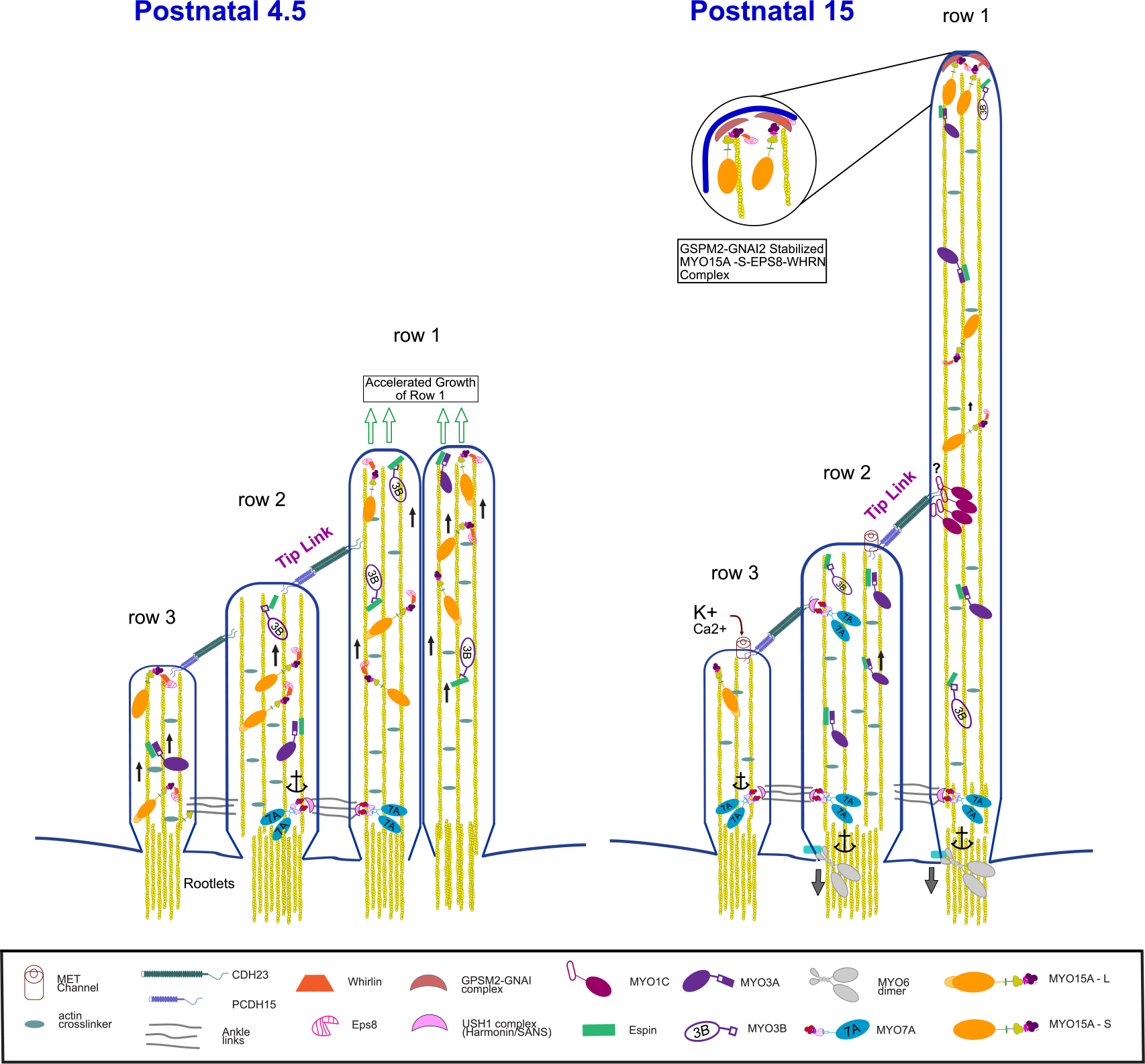
Diagram illustrating the roles of myosins in controlling the length of stereocilia, linking adjacent stereocilia and anchoring the tip link at postnatal day 4.5 (left) and postnatal day 15 (right). MYO3A/B play a role in the transport of the actin bundling protein ESPN that regulates the length of the growing stereocilia. MYO15A also acts as a transporter, carrying the adaptor WHRN and the actin regulator Eps8 to the tips of all stereocilia at P4.5 to promote stereocilia growth. The long isoform MYO15A-L is localized most notably in row 1 (green arrows) at P15 where it forms with Eps8 and WHRN a complex with GPSM2-GNAI complex that stimulates actin polymerization activity and drives stereocilia elongation. In contrast, the short MYO15A-S isoform is found only in rows 2 and 3 where it stabilizes these shorter stereocilia. Several MYO1C are likely associated at the upper tip link density, clustered by an unknown mechanism (indicated by ?) where it contributes to slow adaptation. MYO7A is also present at the upper tip link density where it serves as the tip link motor, tensioning the MET channel. MYO7A also associates with ankle links that contribute to holding the hair bundle together. MYO6 is concentrated at the base of the stereocilia in the actin-dense rootlets where it anchors the membrane to the actin-rich cuticular plate (not shown).
