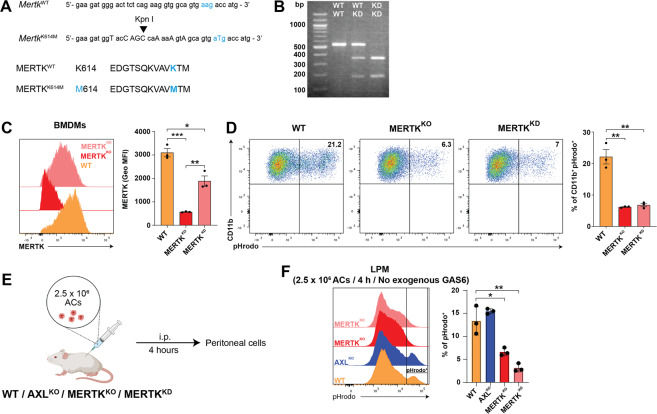
Fig. 4. MERTK kinase activity is essential for clearance of apoptotic cells in vivo.
A (top) targeted codon in Mertk for the generation of MertkK614M/K614M is indicated in blue. A KpnI restriction enzyme site was engineered to aid PCR-based genotyping. (bottom) Amino acid sequence of the targeted region, indicating the introduced mutation at Lysine (K) 614 for Methionine (M) 614. B Diagnostic PCR results, after DNA amplification and digestion with KpnI. The WT allele yields one 548 bp product and the mutant allele yields a 184 and a 364 bp band. C Representative histograms showing expression of MERTK in bone marrow-derived macrophages from mice with the indicated genotypes. Bar graphs show geometrical mean fluorescence of MERTK. Shown is mean with SEM and individual samples. D Representative flow cytometric analysis of efferocytosis with bone marrow-derived macrophages from mice with the indicated genotypes. Macrophages and ACs were co-incubated for 1 h in the presence of serum at a ratio of 1:6 and analyzed afterwards for pHrodo signal. Bar graphs show mean with SEM and individual samples. E Experimental set-up to study contribution of AXL and MERTK for efferocytosis in the murine peritoneum. ACs (2.5 × 106) were injected intraperitoneally into mice of indicated genotype. After 4 h PECs were analyzed via flow cytometry. Created with BioRender.com. F Representative histograms for pHrodo-Red upon injection of ACs into mice of indicated genotype (Gated on CD19−, Ly6G−, and F4/80+ live cells). Frequency of pHrodo+ cells. Bar graphs show mean with SD and individual samples. Data were representative of two individual experiments (n = 3–5).