FIGURE 3.
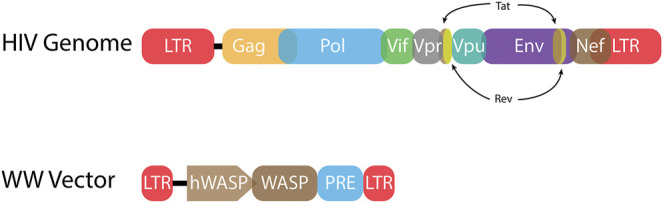
HIV-1 proviral genome and lentiviral vector genome. (Top) The HIV-1 proviral genome (HIV Genome) has long terminal repeats (LTRs) at each end. These non-coding sequences include the terminal sequences that are bound by integrase. The LTRs also encode sequences necessary for viral gene expression including transcription factor binding sites and a TATA box to initiate RNA Pol II transcription. Every retrovirus includes gag, pol, and env genes. These genes encode the structural, enzymatic, and envelope proteins, respectively. HIV-1 also has six accessory genes. Two of these genes, tat and rev, are spliced. (Bottom) A representative lentiviral vector (WW Vector) for treatment of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) encodes the WAS protein (WASP) gene driven by the human WASP promoter (hWASP) (Aiuti et al., 2013). The post-transcription regulatory element (PRE) mediates export of unspliced mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation (Zufferey et al., 1999). Much of the LTR sequences have been deleted, including transcription factor binding sites, yielding a self-inactivating (SIN) vector.
