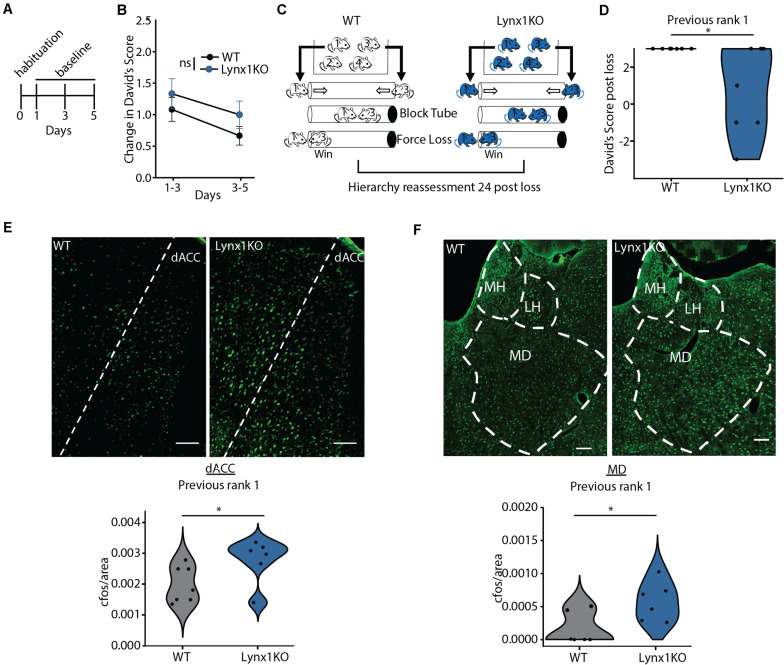
FIGURE 2.
Cortical plasticity modulator Lynx1 limits experience-dependent plasticity of social hierarchy in adult mice. (A) Adult WT or Lynx1KO mice were tested in a round-robin design to assess dominance between all pairs in a cage. Mice were habituated to the tube and then baseline hierarchy was assessed every other day for 5 days. Baseline day 1 was training. (B) Baseline hierarchies showed no significant differences in change in David’s Score (DS) between genotypes (generalized linear model, p = 0.323, n = 36 Lynx1KO from 9 cages, n = 48 WT from 12 cages). (C) Experience-dependent changes in hierarchy were assessed by altering the outcome of the rank 1 vs. 3 match-up by blocking the tube, forcing the rank 1 animals to lose. Hierarchies were reassessed 24 h later. (D) WT previous rank 1 mice maintained their rank following loss while Lynx1KO mice showed significantly reduced DS 24 h post loss (Wilcoxon signed rank test, ∗p = 0.03, n = 7 WT mice, 7 Lynx1KO mice). (E) Dorsal Anterior Cingulate (dACC) shows significantly increased c-Fos labeling in adult Lynx1KO mice following forced loss (two-tailed un-paired student’s t-test, ∗p = 0.05, n = 7 WT mice, n = 6 Lynx1KO mice). (F) Mediodorsal thalamus (MD) shows significantly increased c-Fos in adult Lynx1KO mice following forced loss (two-tailed unpaired student’s t-test, ∗p = 0.02, n = 7 WT mice, n = 6 Lynx1KO mice).