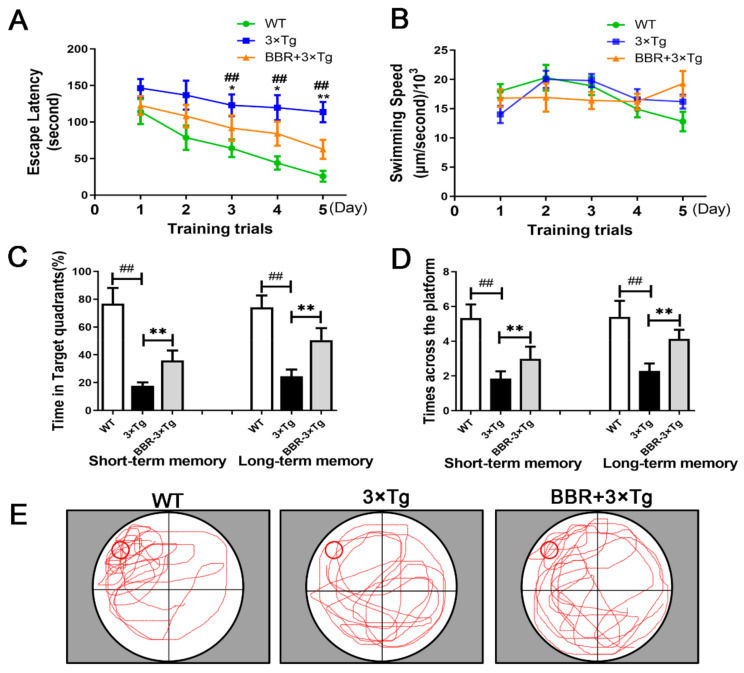
Figure 2.
A Morris water maze task was used to evaluate the effect of berberine on the spatial learning and memory of 3×Tg AD mice. (A) In five-day training trial, the escape latency of each mouse was measured. (B) There were no significant differences in swimming speed across the three groups. (C) In the probe trail, the frequency at which the mouse passed through the submerged platform placement area during the training trial was recorded. (D) Time spent searching for the pre-placed platform in the target quadrant, in both the short- and long-term memory tests. (E) The swimming tracks of the mice from the three groups made in the water tank on the last day of the test. WT, wild-type mice, 3×Tg, 3×Tg AD mice; BBR + 3×Tg; 3×Tg AD mice were given BBR at 100 mg/kg/day. One-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post-hoc test were used to analyze all the data, which are presented as mean ± SD; n = 12 animals/group. * p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, 3×Tg AD group vs. WT group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, BBR treated 3×Tg vs. 3×Tg group.