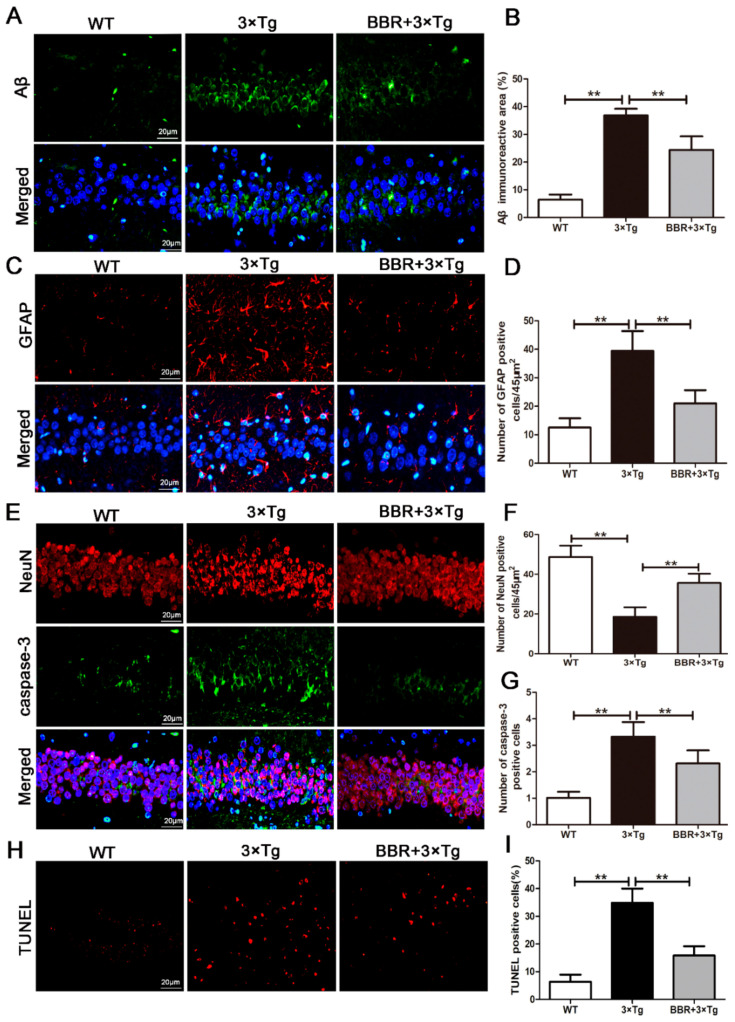
Figure 3.
BBR reduced the production of Aβ and inhibited apoptosis in the brains of 3×Tg AD mice. (A) Immunofluorescence of Aβ (green) in the hippocampi of mice from the three groups. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Quantification of Aβ immunoreactivity in the hippocampi of mice. (C) Immunofluorescence of GFAP (red) in the hippocampi of mice from the three groups. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Quantification of GFAP immunoreactivity in the hippocampi of mice. (E) Immunofluorescence of NeuN (red) and Caspase-3 (green) in the hippocampi of mice from the three groups. Scale bar: 20 μm. (F) Quantification of NeuN and Caspase-3 immunoreactivity in the hippocampi of mice. (G) Quantification of Caspase-3 immunoreactivity in the hippocampi of mice. (I) The number of TUNEL-positive neurons in each group was averaged. (H) The number of TUNEL-positive neurons (red). Scale bar: 20 μm. WT, wild-type mice; 3×Tg, 3×Tg AD mice; BBR + 3×Tg; 3×Tg AD mice were given BBR at 100 mg/kg/day. One-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post-hoc test were used to analyze all the data, which are presented as mean ± SD; n = 12 animals/group. ** p < 0.01.