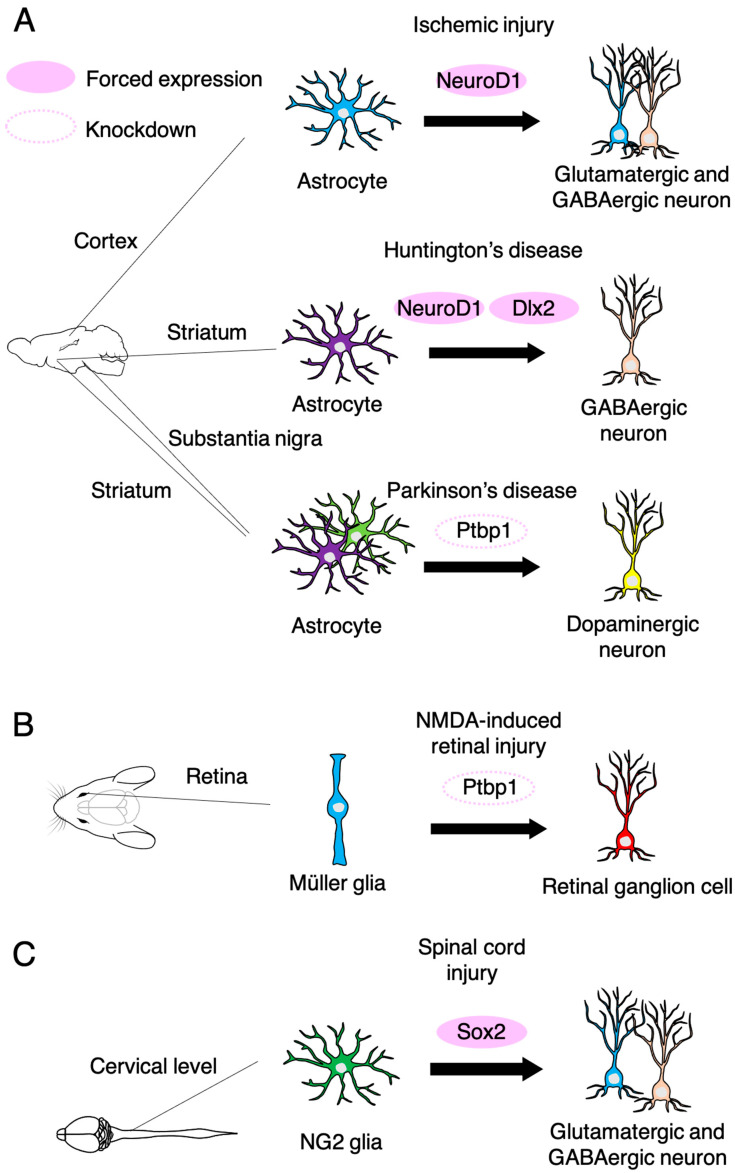
Figure 4.
In vivo neuronal reprogramming from non-neuronal cells in the adult brain, retina and spinal cord. (A) NeuroD1 converts reactive astrocytes to both glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the cortex after ischemic stroke induced by cortical injection of endothelin-1, leading to neurological recovery. In Huntington’s disease model mice, combinatorial expression of NeuroD1 and Dlx2 converts striatal astrocytes into GABAergic neurons and restores motor function. Downregulation of Ptbp1 converts striatal astrocytes into dopaminergic neurons, inducing motor functional recovery. (B) Ptbp1 downregulation converts Müller glia into retinal ganglion cells in NMDA-induced retinal injury model mice, and thereby, repairs the visual function. (C) Forced expression of Sox2 converts NG2 glia into both glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the injured spinal cord, promoting functional recovery.