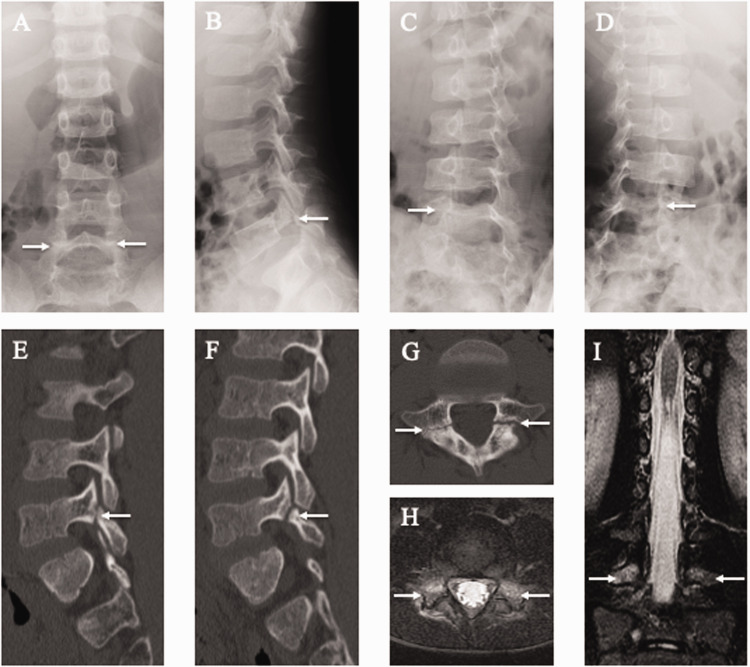
Figure 1.
Results of lumbar spine radiography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the 7-year-old first-born son. Spondylolysis (white arrows) is observed at the fifth lumbar vertebra (L5) on posteroanterior (a), lateral (b), 45° right anterior oblique (c), and 45° left anterior oblique (d) radiographs and right parasagittal (e), left parasagittal (f), and axial CT images parallel to the L5 vertebral arch (g). Axial short tau inversion recovery (STIR)-MRI parallel to the L5 vertebral arch (h) and coronal STIR-MRI (i). Note the signal hyperintensity (white arrows) in the pedicle, indicating marrow edema. This is a sign of an early-stage stress fracture of the pars interarticularis.