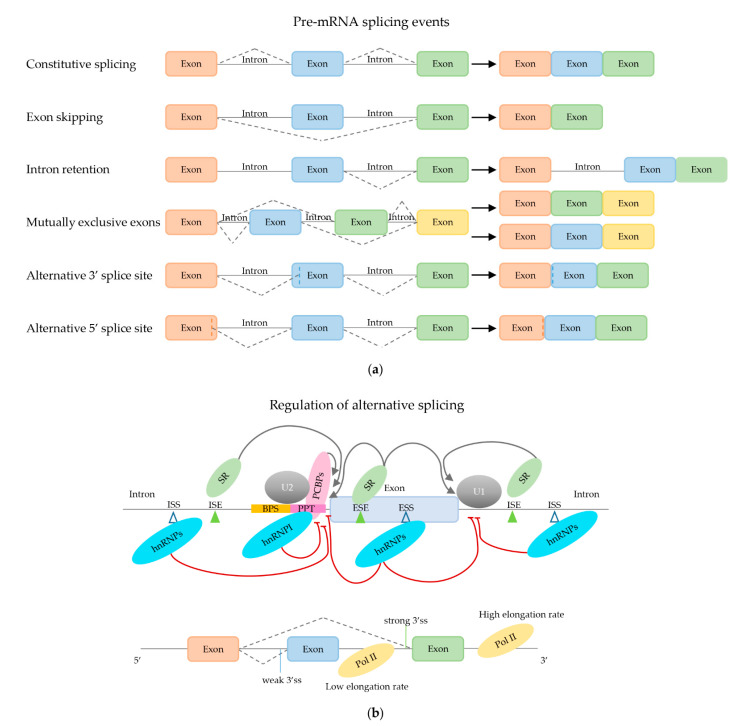
Figure 4.
Pre-mRNA splicing events and regulation of alternative splicing. (a) Schematic representation of constitutive and common types of alternative splicing events. (b) Pre-mRNA splicing regulation. Upper figure: Alternative splicing is mainly regulated by trans-acting splicing factors (such as hnRNPs and SR proteins, which usually inhibit and promote splice site usage, respectively) binding to cis-acting splicing regulatory elements (ESE, ISE, ESS and ISS) on the pre-mRNA substrate. Lower figure: alternative splicing also depends on the elongation rate of RNA polymerase II (Pol II). A low elongation rate of RNA Pol II might provide more opportunities to weak 3′ss usage; while a high elongation rate of RNA Pol II might give priority to strong 3′ss usage. Open triangle: splicing silencer element; filled triangle: splicing enhancer element; arrow: promoting; –I: inhibiting.