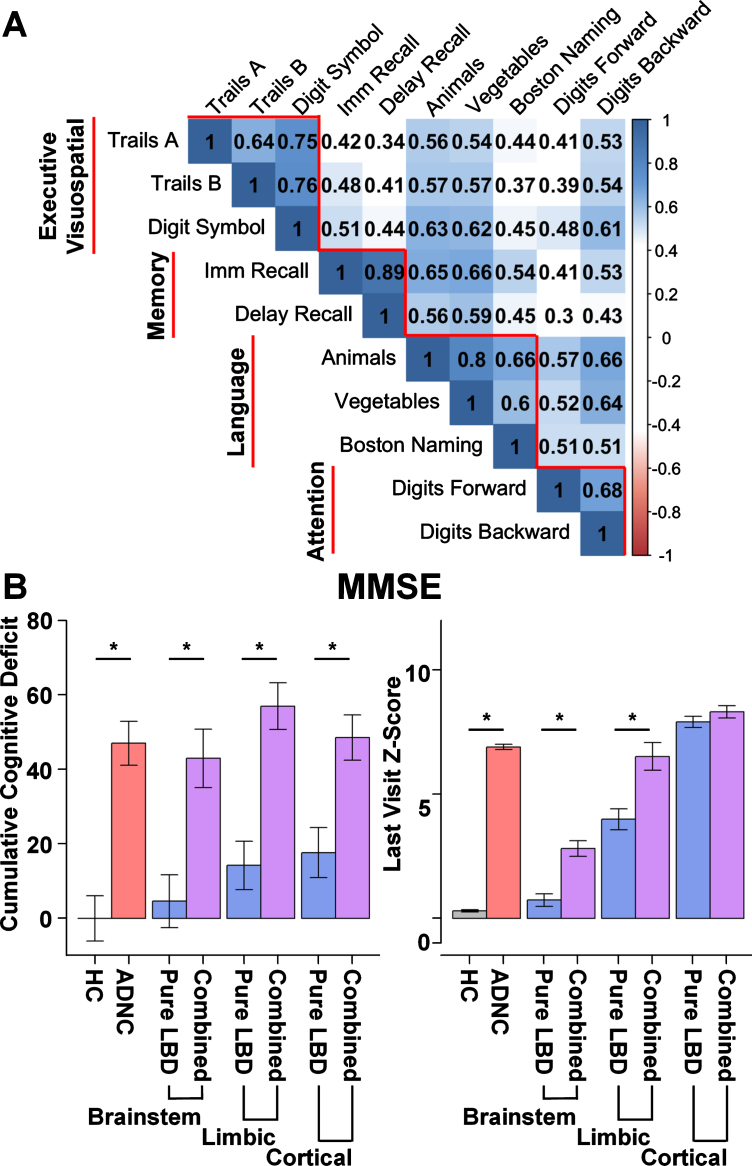
Fig. 2.
Neuropsychological correlations and cumulative global deficit by group. A) Correlation plot depicting greater within domain correlations relative to between domain correlations among neuropsychological tests. Subtests (horizontal) contributing to each domain score (vertical). Executive Visuospatial domain includes: Trails A, Trail Making Test A time; Trails B, Trail Making Test B time; Digit Symbol, Digit Symbol Coding from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale –Revised. Memory domain includes: Imm Recall, Logical memory Immediate Recall; Delay Recall, Logical Memory Delayed Recall. Language domain includes: number of correct words on Animal and Vegetable List generation; score on the modified Boston Naming Test (30 odd item version); Attention Domain includes: Digits Forward, Digit Span Forward total score Wechsler Memory Scale –Revised (WMS-R); Digits Backward, Digit Span Backwards total score from the WMS-R. B) Cumulative global deficit on Mini-Mental Status Exam (MMSE) and average MMSE Z-score at the participant’s last visit (within 2 years of death) by group. Cumulative global deficit is significantly greater for Alzheimer’s disease neuropathologic change (ADNC, red) and the combined ADNC and Lewy body disease groups (ADNC/LBD, purple) relative to Healthy Controls (HC, gray) and LBD only (blue), irrespective of stage of LBD (Brainstem, Limbic, or Cortical).