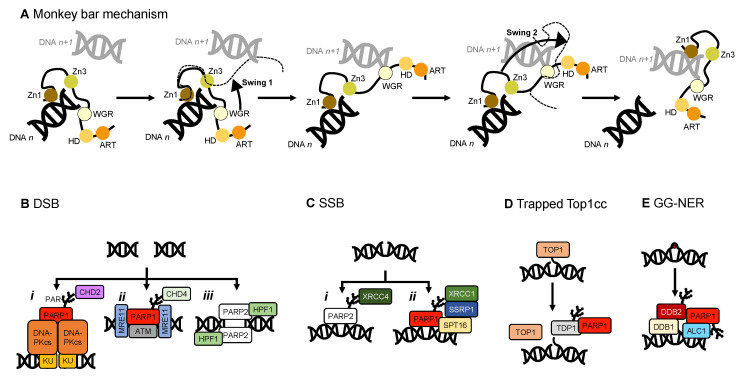
Figure 6.
A schematic showing how PARP1 recognises DNA damage, and examples of the roles of PARP1 and PARP2 in initiating DDR and chromatin remodeling. (A) The monkey bar mechanism [99]; (B) PARP1/2 initiating DSB repair. i. PARP1 interacts with DNA-PK [79] and recruits the chromatin remodeler CHD2 [174] in the canonical NHEJ pathway. ii. PARP1 plays a role in the alternative NHEJ pathway, interacting with MRE11 (part of the MRN complex, [84]), ATM, and recruiting the CHD4 subunit of the NuRD complex [166,167]. iii. PARP2 recognises a DSB along with HPF1 [53,150]; (C) PARP1/2 initiating SSB repair. i. PARP2 plays a role in recognising SSBs and recruiting XRCC4 [175]. ii. PARP1 can also recognise SSBs and recruit XRCC1 [78,176], and subsequently the FACT complex (SSRP1 and SPT16; [176]); (D) PARP1 recruits TDP1 to release trapped TOP1 cleavage complexes (Top1cc) [79]; (E) PARP1 is involved in global genome nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER), recruiting DNA damage-binding protein 1 and 2 (DDB1/2) and the chromatin remodeler ALC1 [177].