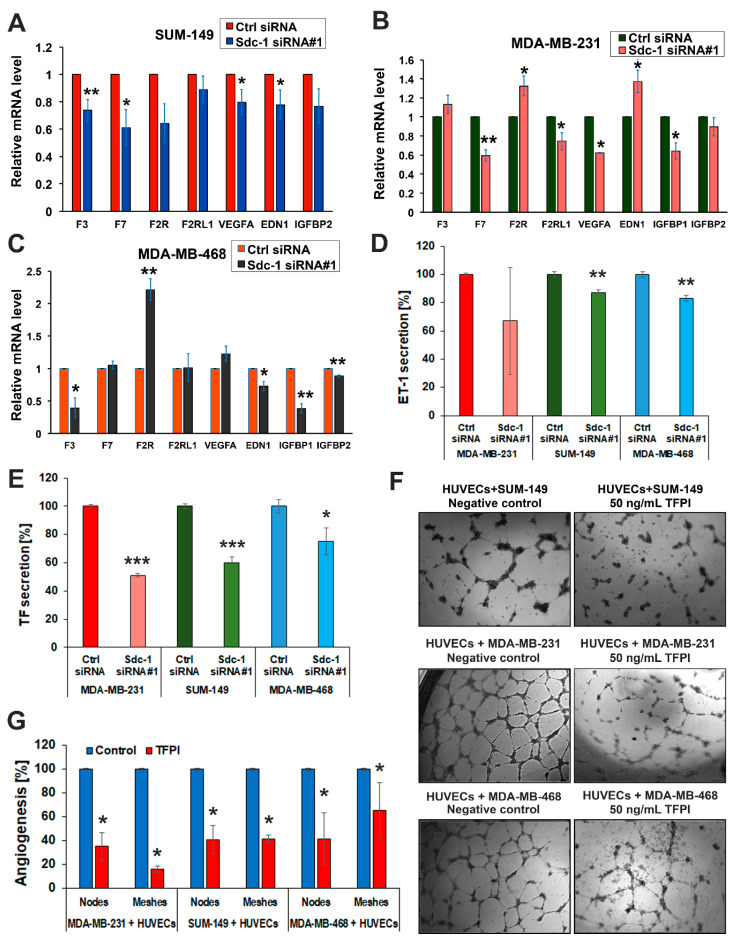
Figure 3.
Impact of Sdc-1 on the gene expression of angiogenic factors and functional impact of tissue factor on angiogenesis. (A–C) Sdc-1 silencing differentially regulates expression of the TF signaling pathway and angiogenic factors in SUM-149, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468 cells as assessed by qPCR. (D) Sdc-1 knockdown decreases EDN1 secretion in SUM-149 and MDA-MB-468 cells. EDN1 secretion was quantified by ELISA in the cell culture supernatants of control and Sdc-1 knockdown SUM-149, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468 cells collected 48 h post-transfection. (E) Sdc-1 knockdown decreases coagulation factor III/TF (F3) secretion in TNBC cells. Coagulation factor III/TF secretion was quantified by ELISA in the cell culture supernatants of control and Sdc-1 knockdown SUM-149, MDA-MB-468, and MDA-MB-231 cells collected 48 h post-transfection. (F) Representative images of the in vitro 3D co-culture model of HUVECs with TNBC cells treated with 50 ng/mL tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). TFPI treatment blunts the ability of tubule formation of HUVECs in co-culture with TNBC cells. (G) Quantitative analysis of nodes and meshes formed by HUVECs in coculture with TNBC cells as analyzed by angiogenesis analyzer software. Data represent the mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3. *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, and * p < 0.05 as determined by Student’s t-test.