Figure 4.
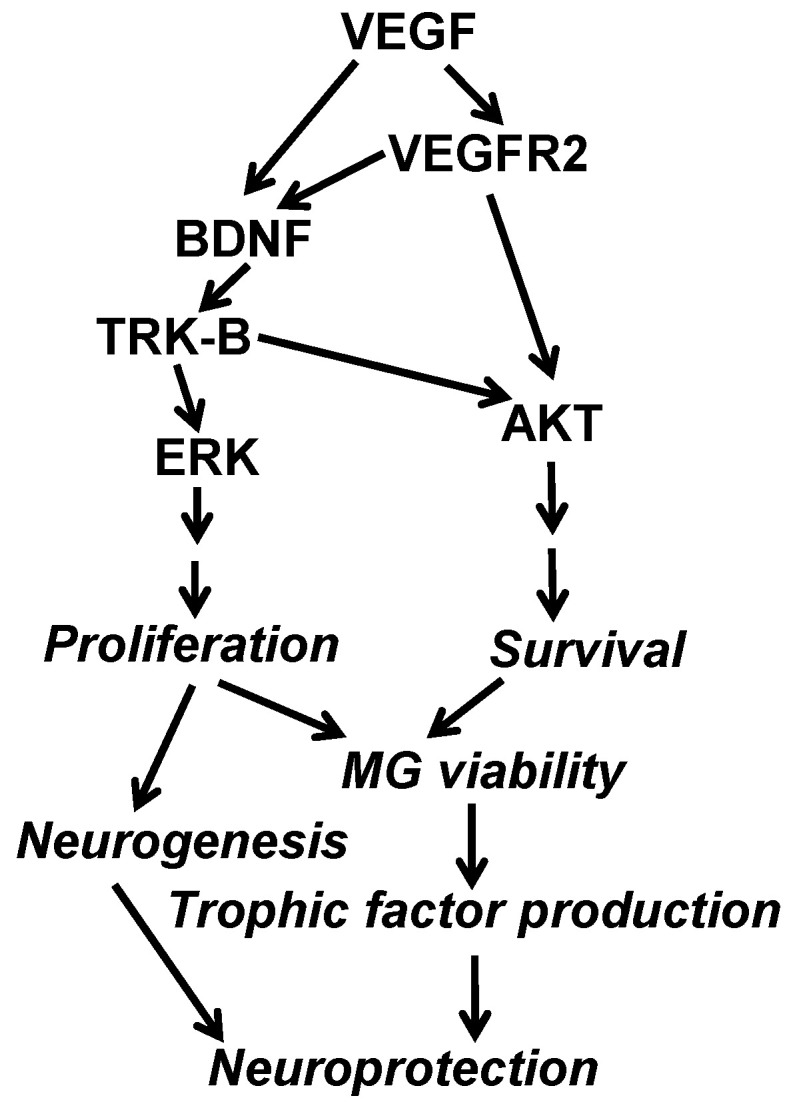
Working hypothesis and mechanisms of VEGF-mediated MC viability and neuroprotection, based on our previous and current work. VEGF plays a cardinal role for neuroprotection in DR and hypoxic retinal disorders through its own action (VEGFR2/AKT-mediated MC survival) and through its downstream neurotrophin-mediated MC viability, including BDNF/TRK-B-mediated MC proliferation and survival. As a result, MCs exert the neuroprotective function by trophic factor production and neurogenesis.
