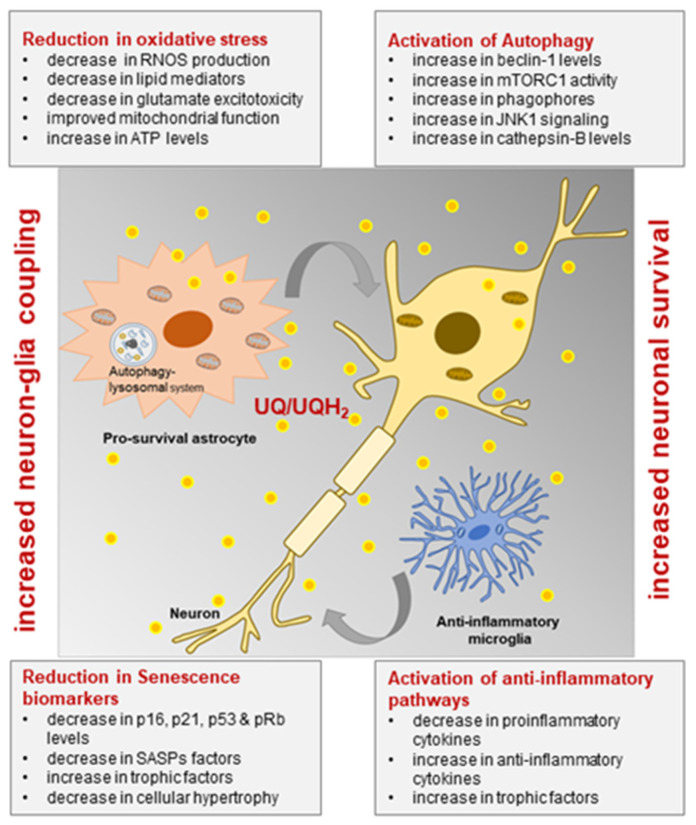
Figure 4.
Schematic illustrating the neuroprotective potential of Ubisol-Q10. Ubiquinone (UQ) is converted to Ubiquinol (UQH2), which is involved in key cellular functions. Neuroprotection could be mediated through modulation of several astrocytic and microglial pathways, for instance reduction of oxidative stress by decreasing reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RNOS), lipid mediators, glutamate excitotoxicity and improving mitochondrial function. Activation of autophagy by increasing beclin-1 levels and up-regulating mTORC1, JNK and cathepsin-B activity. Decreasing cellular senescence by reducing growth arrest and secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators and increasing secretion of neurotrophic growth factors. Increasing anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β. These effects result in restoring cellular homeostasis, leading to increased neuron-glia coupling and neuronal survival.