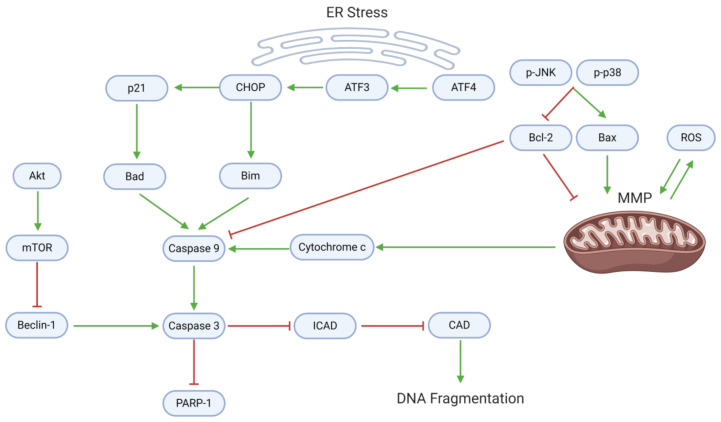
Figure 5.
Proapoptotic mechanisms, which involve mitochondrial dysfunction, ER stress, and caspase activation, are suppressed in GBM. Dysregulation of mitochondrial homeostasis (often through oxidative imbalance) leads to the release of cytochrome c, a caspase activator. ER stress upregulates activating transcription factors; in turn, ATFs activate CHOP, p21, and proapoptotic proteins that enhance caspase activation. Active caspase 9 (along with Beclin-1) cleaves caspase 3, which enforces apoptosis and DNA fragmentation. In proliferating GBM cells, however, the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 directly inhibits caspase 9, while mTOR inhibits Beclin-1.