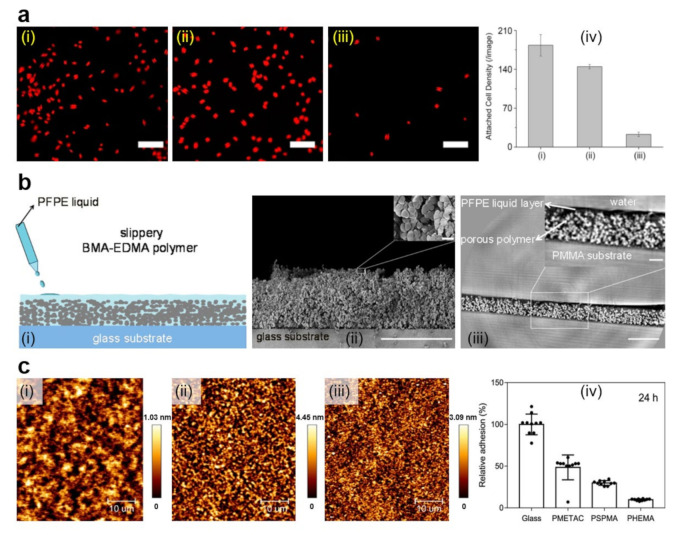
Figure 4.
(a) Fluorescence images (i–iii) and quantification (iv) of A. coffeaeformis diatoms that succeeded to attach on the (i) untreated stainless steel, (ii) PDA-coated stainless steel, and (iii) PEG-based film. Each point is the mean of 60 counts on three replicate samples in (iv). Scale bars represent 50 μm. (b) Schematic representation of the fabrication of slippery P(BMA-co-EDMA) surface by infusion of the porous polymer with the PFPE fluid (i), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images depict a cross-section and the porous morphology of the P(BMA-EDMA) surface (ii) and reconstructed X-ray propagation phase-contrast tomography image displaying the cross-section of the slippery P(BMA-EDMA) surface underwater (iii). Scale bars are 100 μm (ii,iii), 2 μm (ii) and 20 μm (iii) in the insets, respectively. (c) atomic force microscopy (AFM) height images depict PMETAC (i), PSPMA (ii), and PHEMA (iii) polymer brushes attached to the glass coverslips and their antiadhesive performance against E. coli compared to naked glass, after an incubation time of 24 h (iv). The relative adhesion of bacteria on the above substrates was normalized with respect to the adhesion on the glass substrate for 24 h. Adapted with permission from ref. [104] (a), ref. [107] (b) and ref. [139] (c).