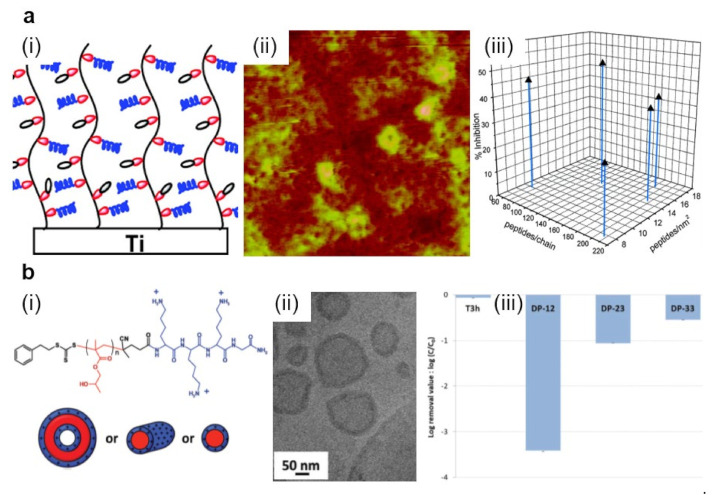
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic representation (i) and AFM topography (ii) depict P(DMA-co-APMA) copolymer chains adopting brush-like conformations on titanium surfaces. Depending on the initial composition ratio between the DMA and APMA monomers and on the peptide density, P(DMA-co-APMA) copolymer exhibits more or less inhibitive effects against bacteria (iii). The size of the AFM image is 3 × 3 µm2. (b) Schematic representation (i) and a cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) image (ii) depict spherical core–shell vesicles that could self-assemble from PLys-b-PHPMA block copolymer. The chemical structure of the copolymer is presented on top of (i). Experimentally observed structures are then able to act against S. epidermidis with high efficiency (iii). Log removal data were obtained after 3 h for the control reactor without any material (T3h) and the reactor with various PLys-b-PHPMA block copolymers. Adapted with permission from ref. [149] (a) and ref. [150] (b).