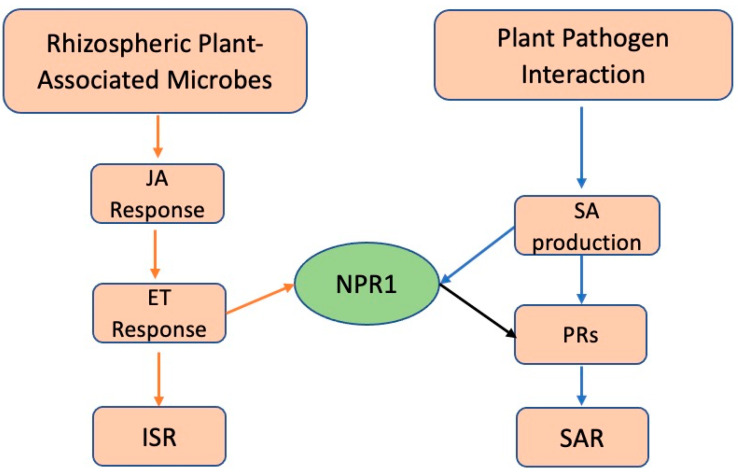
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the common signal-transduction pathways leading to pathogen-induced systemic acquired resistance (SAR) and rhizosphere-mediated induced systemic resistance (ISR) inspired by [114] for Arabidopsis thaliana but applicable to plants in general. Crosstalk between the two pathways occurs through the activation of NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES1 (NPR1). Non-pathogenic plant-associated microbes, usually from the rhizosphere, can trigger the SAR pathway as well as ISR. In the rhizosphere-mediated ISR pathway, components from the jasmonic acid (JA) and ethylene (ET) responses act in sequence to activate a systemic resistance response (orange arrows). Pathogenic agents could activate the pathogen-induced SAR, through the activation of NPR1 (blue arrows), leading to the expression of PATHOGENESIS-RELATED genes (PRs) (black arrow). NPR1 also mediates crosstalk between the SA signaling pathway.