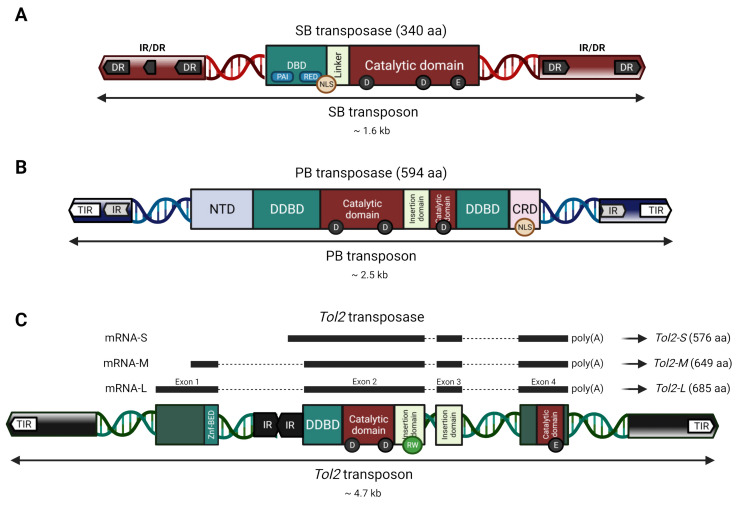
Figure 2.
Organization and functional domains of the Sleeping Beauty (SB), piggyBac (PB), and Tol2 autonomous transposable elements and transposases. Transposons are depicted as a double-stranded DNA helix flanked by TIRs (arrows). Transposases within each autonomous transposon appear with their respective protein domains (rectangles) after transcription and translation. (A) The SB transposon is flanked by TIRs in an inverted repeat/direct repeat (IR/DR) structure (dark grey and red arrows). The SB transposase is depicted with its domains, including a nuclear localization signal (NLS, orange circle), and the PAI and RED subdomains (blue rounded rectangles) of the DNA binding domain (DBD, green rectangle). (B) The PB transposon is flanked by its TIRs and subterminal IRs (white, blue and light grey arrows). The PB transposase is shown with its domains and NLS (orange circle). (C) The Tol2 transposon is flanked by its TIRs and subterminal regions (white and black arrows). The autonomous Tol2 transposon contains an internal Angel element (IR black arrows) and the Tol2 transposase coding sequence with its four exons coding for different protein isoforms (black bars). Tol2 is shown with its domains, as well as the typical RW-motif (light green circle) of the members of the hAT family. The structure of Tol2’s putative functional domains was matched with the coding sequence based on the general domains of the hAT family members [28], the nucleotide positions on the Tol2 DNA sequence (DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. D84375), and previous analysis of Tol2 [29,30,31]. NTD: N-terminal domain; CRD: Cysteine-rich domain; DDBD: Dimerization and DNA-binding domain; Znf-BED: BED-type zinc finger domain.