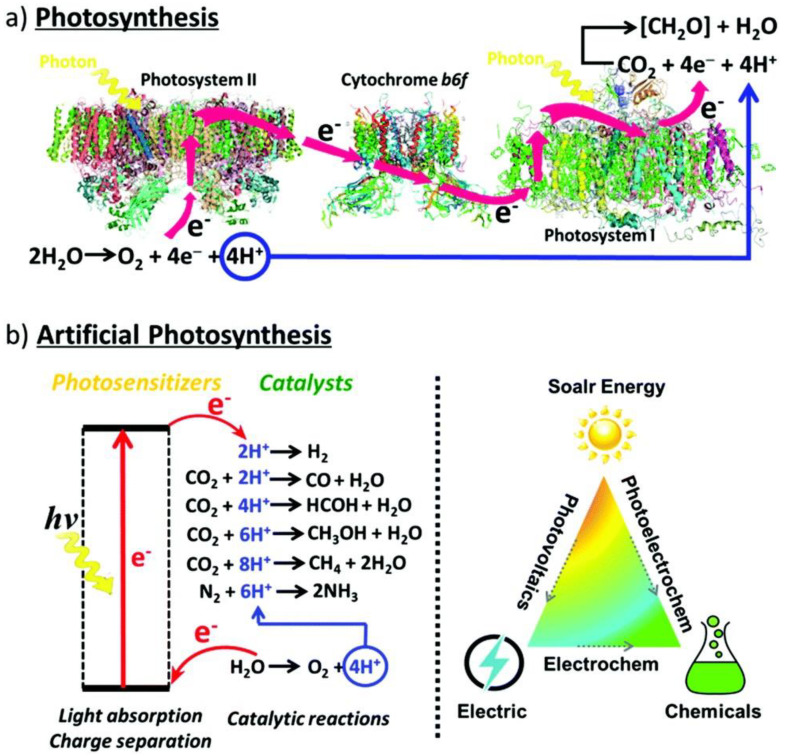
Figure 1.
(a) Photosynthesis is enabled through the collaborative efforts of two photosynthetic complexes, PSI and PSII, where PSI serves as the reaction center and light harvesting complex and PSII is the site of water oxidation. Thus, H2O is oxidized in PSII into O2 releasing four protons and electrons, respectively, that are transferred via cytochrome b6f, an enzyme in plant chloroplasts, to PSI where they are consumed by CO2 reduction to produce carbohydrates. (b) Artificial photosynthetic systems for photocatalysis are being developed to mimic and provide for the very same conversion of solar energy through alternative energetic pathways and selectivity for fundamental and desirable chemical reactions, including water splitting, CO2 photoreduction, and the degradation of harmful organic pollutants. Reprinted with permission from Ref [10] with attribution and adherence to Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence. Copyright Royal Society of Chemistry (2019).