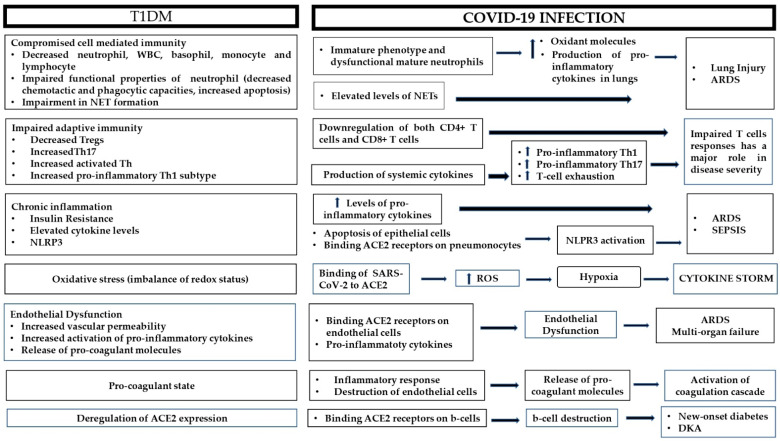
Figure 1.
Possible pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for adverse outcomes during COVID-19 infection in patients with type 1 diabetes. ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome; ACE2: angiotensin converting enzyme 2; DKA: diabetic ketoacidosis; NET: neutrophil extracellular trap; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3; ROS: reactive oxygen species; Th: T-helper; Tregs: regulatory T-cells; WBC: white blood cells.