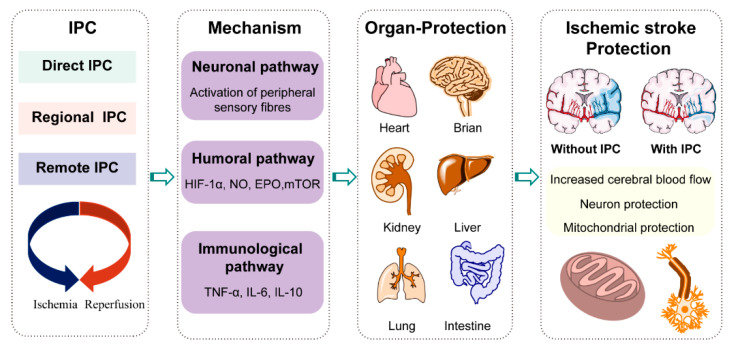
Figure 1.
General description of ischemic preconditioning (IPC), in which several cycles of brief non-lethal ischemia and reperfusion are applied either directly, regionally, or remotely. Through neuronal, humoral, and immunological pathways, IPC confers protection against subsequent, more severe, and lethal ischemia. The ischemic protection of IPC has been applied in various organs, such as the heart, brain, kidney, liver, lungs, and intestine. For ischemic stroke, IPC can reduce the infarct size and improve prognosis, which is supported by increasing the cerebral blood flow (CBF), protecting mitochondrial function, and maintaining neuronal activity.