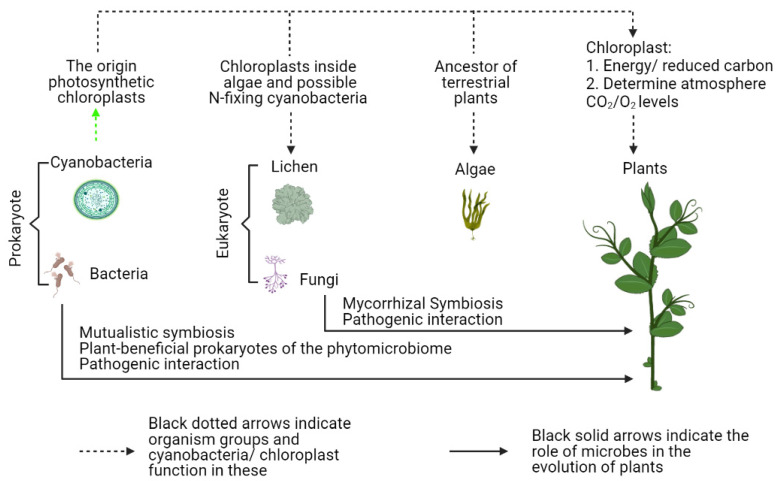
Figure 1.
A range of microorganisms contribute to plant function, allowing them to become the dominant terrestrial primary producers, such as crop plants. This includes prokaryotes becoming organelles (mitochondria and chloroplasts), with cyanobacteria focused on because of their pivotal role in giving plants photosynthetic ability, through chloroplasts, and a range of other microbes forming other beneficial (plant growth promotion microbes) and negative (pathogens) associations with plants. The combination of fungi, algae (with cyanobacteria-derived chloroplasts) and, at least sometimes, cyanobacteria, resulted in a parallel “organismal” development.