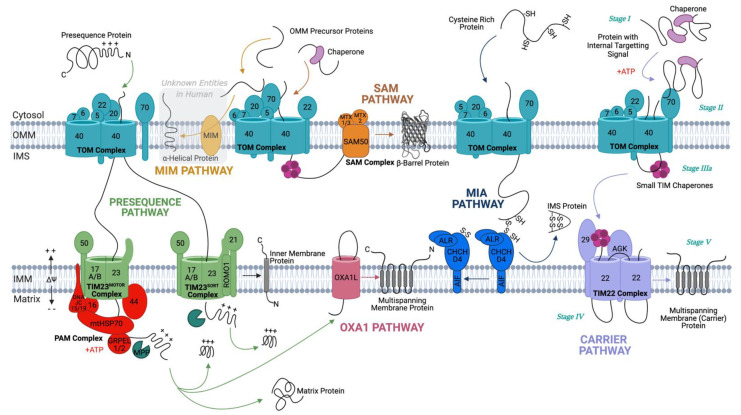
Figure 1.
Overview of human mitochondrial protein import pathways. The TOM complex acts as the central entry gate for precursor proteins to enter the IMS, where they are diverted into one of five pathways, depending on their structure, function, and target destination. The MIM pathway (only currently understood in yeast) is an exception in that proteins usually do not cross the Tom40 channel. Instead, OMM α-helical proteins are recognised by Tom70 and transferred through MIM to be inserted into the OMM. The five major pathways proteins take after crossing the TOM channel are the following. The presequence pathway: Presequences containing precursor proteins are transported via the presequence pathway. Of these proteins, proteins with a hydrophobic sorting sequence are inserted into the IMM by the TIM23SORT complex, whereas hydrophilic matrix proteins are pulled through the TIM23MOTOR complex, with the help of the PAM complex and ATP hydrolysis cycles. The presequences of both these groups of proteins are cleaved by MPP on the matrix side. The OXA1 pathway: N-terminally inserted multispanning membrane proteins, once passed through TIM23MOTOR and cleaved by MPP, are passed to OXA1L, which inserts them into the IMM in the N-terminal formation. OXA1L is also responsible for the insertion of mtDNA encoded proteins into the IMM. The SAM pathway: β-barrel proteins are transported to the TOM complex by cytoplasmic chaperones. They are then passed through the TOM complex and received by small TIM chaperones on the other side for insertion into the OMM by the SAM complex. The MIA pathway: Cysteine-rich proteins in an unfolded, reduced state are passed via the TOM complex to the MIA complex, which inserts disulphide bonds in them, allowing them to reside in a folded, oxidised state in the IMS. Carrier pathway: Proteins with internal targeting signals are protected in the cytosol by cytosolic chaperones (Stage I), which pass them to the TOM complex (Stage II). They are received on the IMS side by small TIM chaperones (Stage III), which transfer them through the IMS to the TIM22 complex (Stage IV) for insertion into the IMM (Stage IV).