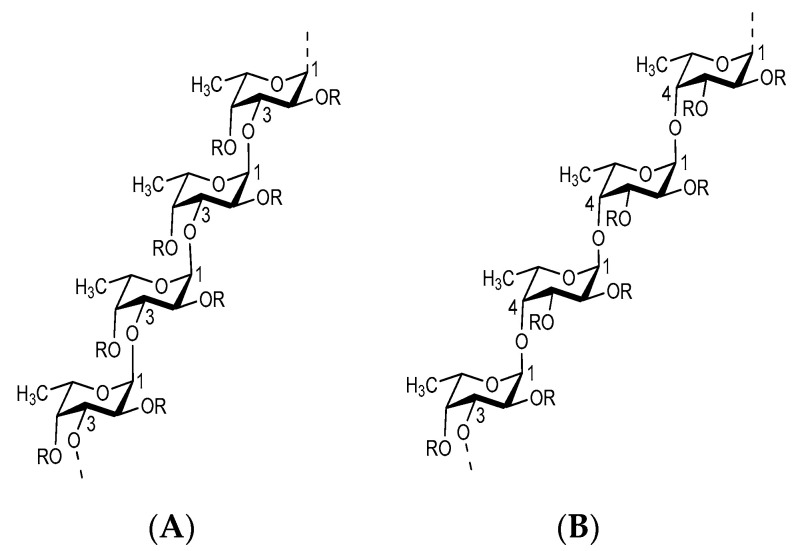
Figure 1.
The chemical structures of fucoidan of two different backbones (A,B). R shows the potential places for attachment of carbohydrate (α-l-fucopyranose and α-d-glucuronic acid) and noncarbohydrate (sulfate and acetyl groups) substituents, adapted from [21].