Figure 1. The general chemical synthesis scheme for conjugating alginate with gelatin and heparin.
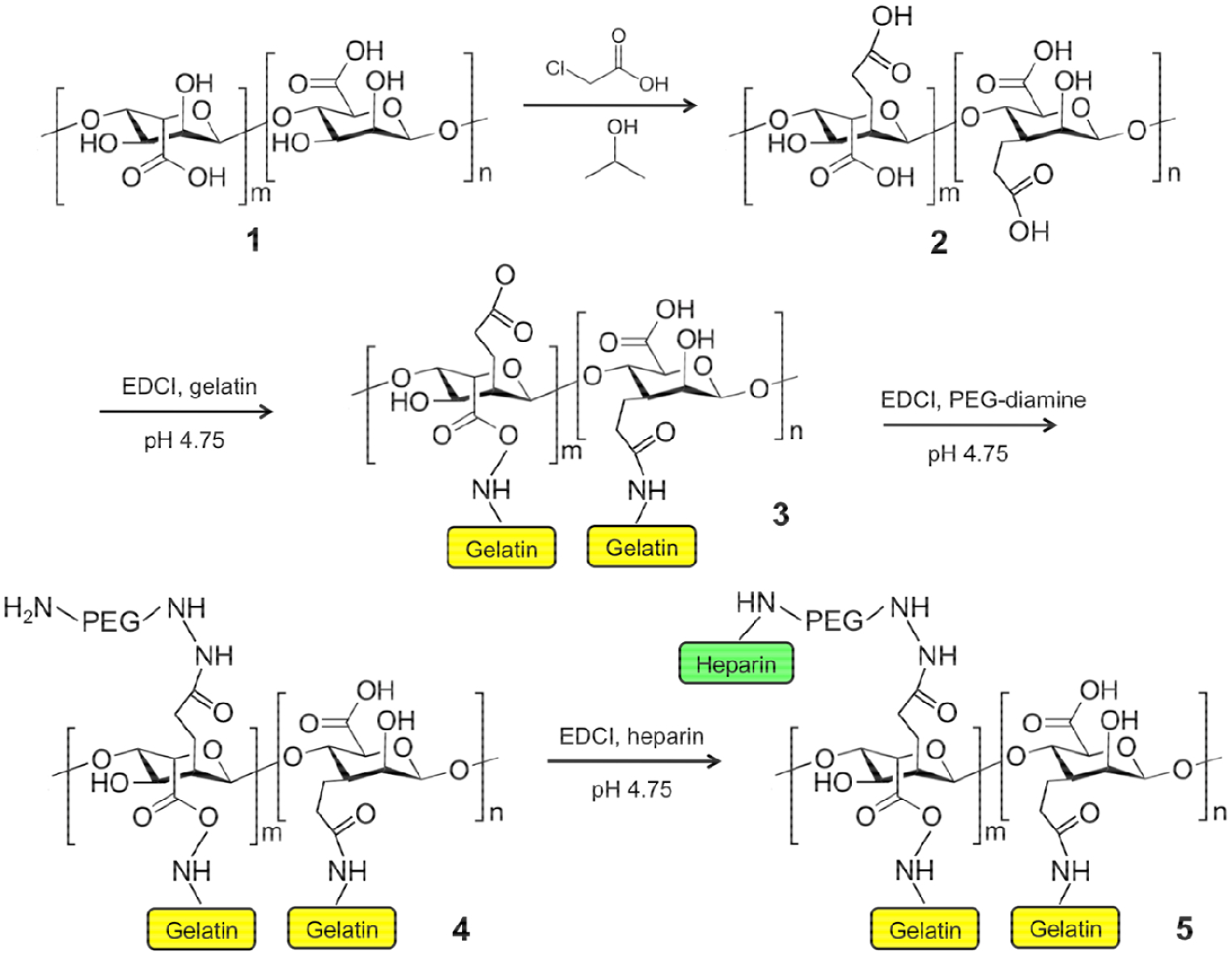
Alcohol groups on the alginate (1) undergo carboxymethylation to provide alginate with increased numbers of carboxylic acid groups (2) for further modification. Gelatin is coupled to the alginate via EDCI chemistry of the gelatin N-terminus amine, resulting in gelatin peptides covalently bound to the alginate (3). Unused carboxylic acid groups on the alginate are then modified with PEG-diamine via EDCI chemistry, (4) after which heparin is bound to the available amine groups of the now pegylated alginate via EDCI chemistry using the carboxylic acid groups on the heparin chains, resulting in alginate covalently modified with both gelatin and heparin (5).
