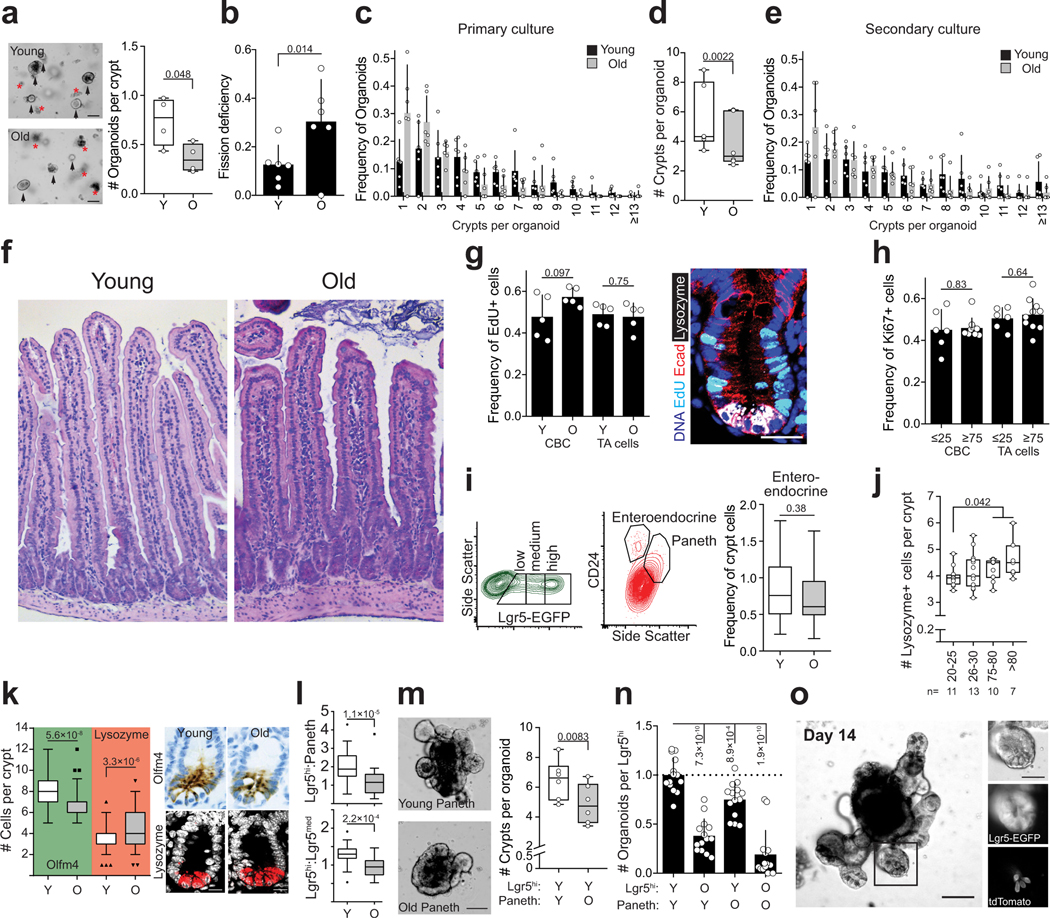
Extended Data Figure 1.
Characterization of aged intestine
a, Organoid forming capacity of crypts from young and old mice (n=4 animals per group). Student’s paired t-test. b, Frequency of organoids unable to form new crypts (fission deficiency) in young and old mice (n=6 animals per group) analysed 5–9 days after isolation. Student’s paired t-test. c, Distribution of regenerative growth capacity of primary organoids from young and old mice (n=6 animals per group). d, Regenerative growth of subcultured secondary mouse organoids (n=6 animals per group). Student’s paired t-test. e, Distribution of regenerative growth capacity of subcultured secondary organoids from old and young mice (n=6 animals per group). f, Representative Hematoxylin&Eosin staining of mouse jejunal sections from young and old animals (4 animals analysed per group). g, Quantification of EdU+ cells in jejunal crypts 2h post administration. Only cells next to Lysozyme+ Paneth cells were quantified as crypt base columnar (CBC) stem cells. Crypt cells that were not touching Lysozyme+ cells were quantified as transit-amplifying (TA) cells (n=5 animals per group). Representative image of crypt stained for EdU (cyan), DAPI (nuclei, blue), Lysozyme (white), and E-cadherin (red). Scale bar 20 μm. h, Quantification of Ki67+ cells in human ileal biopsies. Cells at the crypt bottom with elongated nuclei next to postmitotic Paneth cells were counted as CBCs. Cells not at the crypt base were considered TA-cells. (n=6 for 20–25 years old donors, n=10 for ≥75 years old donors). i, Representative gating of Lgr5hi, Lgr5med, Lgr5lo, Paneth and Enteroendocrine cells (in relation to Fig. 1c). Quantification of enteroendocrine cells (n=30 young, n=26 old). For FACS gating strategy, see Supplemental Data 1. j, Analysis of human ileal biopsy material for Lysozyme+ Paneth cells (n-values for analysed samples shown). k, Immunostaining and quantification of Olfm4+ stem and progenitor cells (green background, n=75 crypts from young and old. 5 individuals per age group) and Lysozyme+ Paneth cells in jejunal crypts (red background, n=115 crypts from young and n=117 crypts from old mice, 5 individuals per age group). Whiskers plotted according to Tuckey’s method. Scale bars 10μm. l, Ratio of Lgr5hi stem cells and Lgr5med progenitor cells and ratio of Lgr5hi stem cells and Paneth cells analyzed by flow cytometry from isolated crypts (n=30 young, n=26 old). Whiskers plotted according to Tuckey’s method. m, Regenerative growth of young Lgr5hi stem cells co-cultured with young or old Paneth cells. Quantification at Day 8–11. (n=6). Representative images are from day 8. Scale bar 100μm, Student’s paired t-test. n, Long-term clonogenicity of young and old Lgr5hi stem cells co-cultured with young and old Paneth cells. Serially passaged organoids were quantified 21 days after initial plating (n=14 animals per age group). Combinations compared to average of young Lgr5hi cells co-cultured with young and old Paneth cells. o, 14 day co-culture of Paneth cells from tdTomato expressing mouse (R26-mTmG) with Lgr5hi stem cells from Lgr5-EGFP-IRES-CreERT2 mouse show long term niche-interactions in organoid culture. Scale bar 100μm. Similar results seen in 3 replicate wells from cocultures of the same mice. Y = mice between 3 and 9 months of age, O = mice over 24 months of age in all experiments. Unless otherwise indicated, line at Box-and-Whisker -plots represents median, box interquartile range and whiskers range. All other data are represented as mean +/− s.d. and conditions compared with two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test, exact P-values shown in corresponding panels. P-values < 0.05 were considered significant.