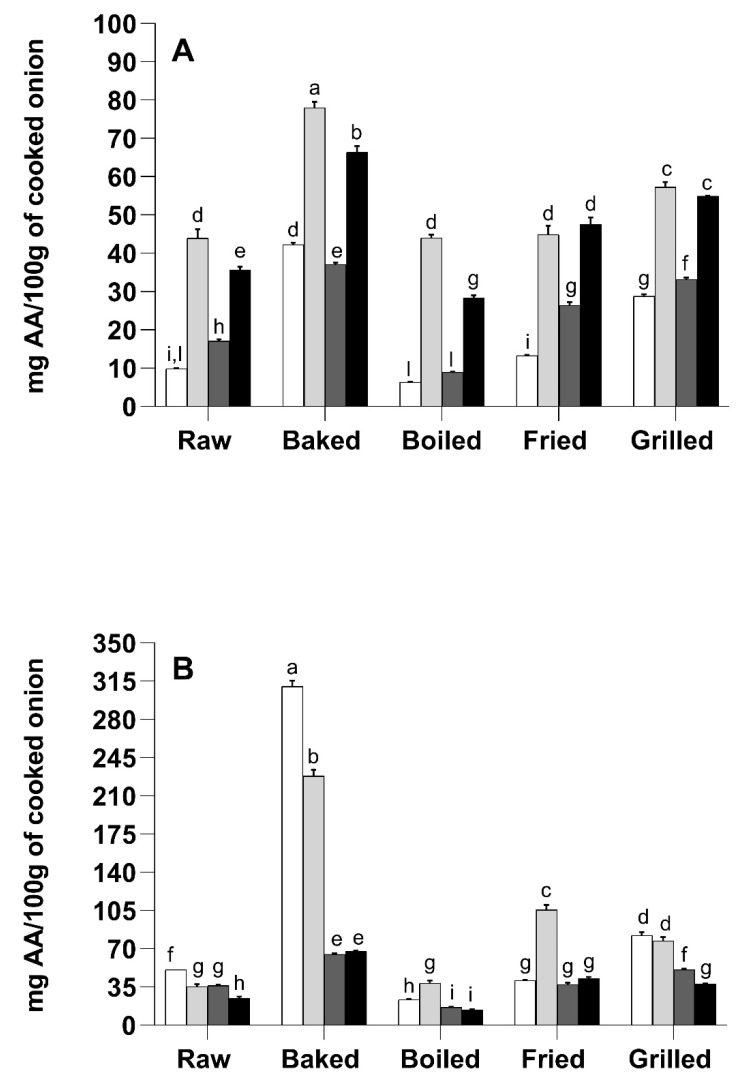
Figure 5.
Effect of different cooking methods and in vitro digestion on yellow-skinned (YSO) and red-skinned (RSO) onions antioxidant activity. (A) YSO antioxidant activity as determined by the ABTS assay in the methanolic/formic acid extract (white) and after in vitro digestion (light grey bars). RSO antioxidant activity as determined by the ABTS assay in the methanolic/formic acid extract (dark grey bars) and after in vitro digestion (black bars). (B) YSO antioxidant activity as determined by the FRAP assay in the methanolic/formic acid extract (light grey bars) and after in vitro digestion (grey bars). RSO antioxidant activity as determined by the FRAP assay in the methanolic/formic acid extract (dark grey bars) and after in vitro digestion (black bars). Results are expressed as mg of ascorbic acid equivalent/100 g of raw or cooked onion. Different letters indicate that the values are significantly different (p < 0.05).