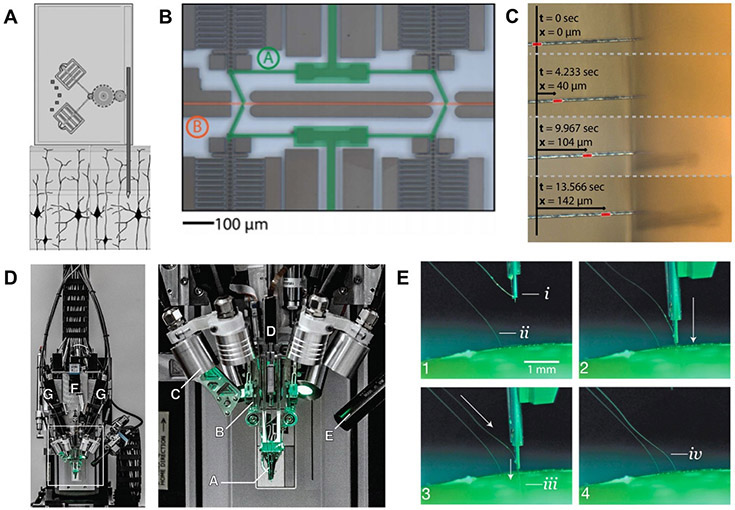
Figure 6.
Electrically-driven microactuated insertion of flexible microelectrodes. (A) Example of the electrostative comb-drive microactuators developed by Muthuswamy et al Reproduced with permission from [163] (Copyright IEEE, 2006). (B) The ‘capacitive finger’ system used to drive (C) carbon fiber microelectrodes into agarose developed by Zoll et al [63]. (D) Surgical electrode stitching robot developed by Neuralinkto implant flexible polyimide multi-channel thread electrodes into brain tissue [164]. (E) Close-up view of electrode stitching process. The threads contain a loop at the end, which provides a handle for the inserting needle to drive them into the brain tissue at a pre-defined depth [164].