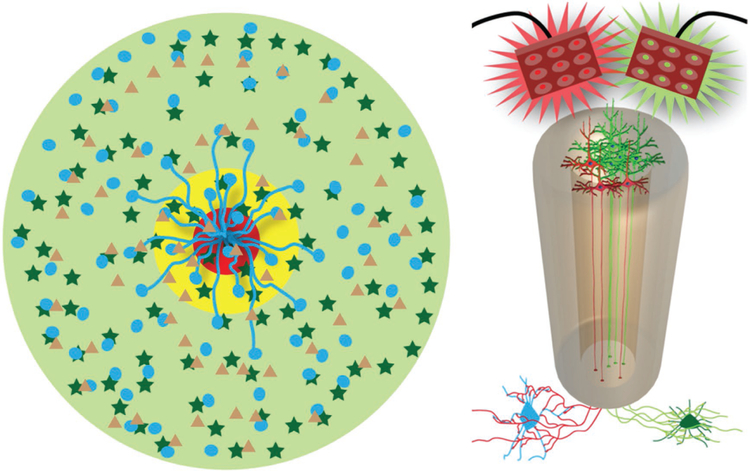
Figure 4.
Mechanisms-of-Action for Axon-Based Living Electrodes: Synaptic Specificity, Biological Multiplexing, and Stability. “Living electrodes” may offer high specificity, as the constructs can be designed to synapse with specific neuronal subtypes, as demonstrated conceptually by living electrode axons synapsing with only circle neurons, not star neurons (left cartoon). This may be exploited in mixed neuron living electrodes where a subpopulation (blue cells) is excited with red light while another subpopulation (dark green cells) could be inhibited by green light (right cartoon). Multiplexing: one living electrode axon can (in theory) synapse with hundreds to thousands of host neurons – creating a significant amplification effect. We currently build living electrodes with 5000–50 000 neurons within a column less than twice the diameter of a human hair. Moreover, living electrodes may offer stability as synaptic integration offers permanence not possible with standard approaches while the biological nature of the constructs may mitigate the chronic foreign body response.