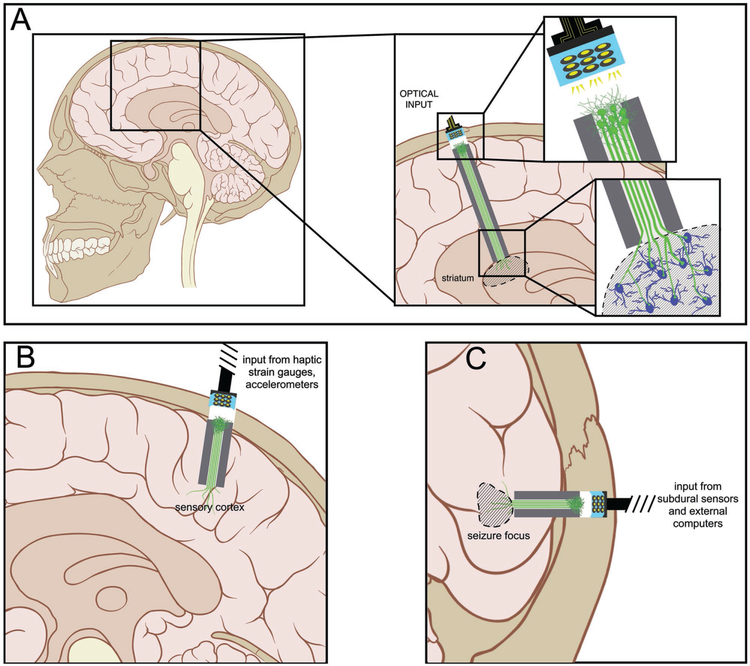
Figure 5.
Potential Applications of Axon-Based Living Electrodes: Custom engineered living electrodes consisting of a phenotypically-controlled populations of neurons extending long axonal tracts through a biocompatible micro-column may be stereotactically transplanted to span various regions to treat particular disease processes. (A) Axons projecting from dopaminergic living electrodes may form synapses within local striatal architecture, and, due to in vitro functionalization with channelrhodopsins, may release dopamine upon optical stimulation of the perikaryal segment at the brain surface. This mimics the substantia nigra pars compacta input to the striatum in a manner that can be externally controlled. (B) Axons from glutamatergic living electrodes may preferentially synapse onto layer IV neurons within primary sensory cortex to convey illusory haptic feedback via surface optical stimulation to achieve closed-loop control of neuromotor prosthetics in patients with paralysis. (C) Axons from GABAergic living electrodes could be implanted to oppose seizure foci such that optical stimulation would cause net suppression of seizure activity in patients with lesional epilepsy.