Figure 5.
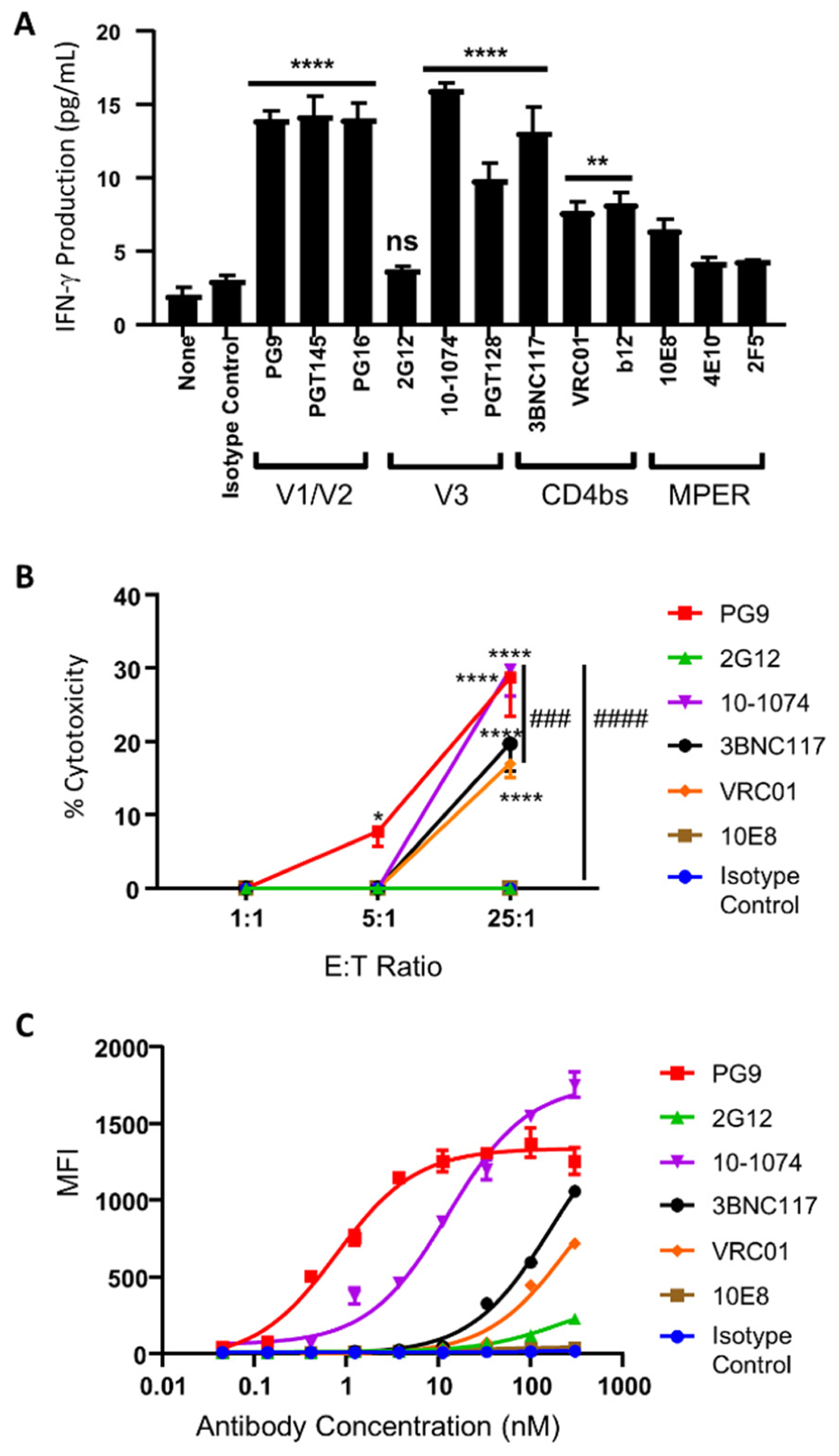
Targeting subtype C gp160+ cells by universal CAR-NK cells. (A) IFN-γ production by anti-DNP CAR-NK cells against subtype C gp160+ cells in the presence of DNP-conjugated bNAbs (2 nM). The concentrations of IFN-γ were determined by ELISA. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. Statistical significance is calculated by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post-hoc test compared with the isotype control. ns: not significant, ** p<0.01, **** p<0.0001. (B) Cytotoxicity of anti-DNP CAR-NK cells against subtype C gp160+ cells at multiple E:T ratios and with different DNP-conjugated bNAbs (2 nM). Data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. Statistical significance is calculated by two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc analysis. * p<0.05, **** p<0.0001 vs. the isotype control. ### p<0.001, #### p<0.0001 comparing % cytotoxicity of 10-1074 to VRC01 and 2G12, respectively, at the 25:1 E:T ratio. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of the binding potency of each bNAb against subtype C gp160-expressing cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate samples.
